Level-1 Report
5 / 6 / 2025
Task :1 Basic UAV Assembly & Components Familiarization
Objective: To write about different materials to assemble a drone with an empty weight of 800g. State the reasons behind material selection and endurance. Calculate the thrust, battery, ESC, and other materials needed for the drone.
Material Selection:
For the drone frame, Carbon fibre was selected due to it's exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, rigidity, and resistance to deformation. It ensures the drone remains lightweight while being capable to withstand mechanical stress during flight. It's non-corrosive properties make it ideal for long-term use in various environments.
Component Selection:
1.Motor
- Model: Ecoll 2814-830(830)
- The Ecoll 2814-830(830) motor is a high-performance brushless outrunner motor designed primarily for RC aircraft.
- No load current is 1.3A @ 10 V.
- The notation 2814 indicates the size of stator i.e 28 is the diameter of stator in mm and 14 is the height of the stator in mm.
- The notation 830 indicates the kv i.e velocity constant the motor runs at speed of 830 rpm at 1 volt.
- The speed of the motor kept slow due to large propellers size which cause increase in the temperature and heat loss in thr system.

Dat Sheet of the Motor

2.Propellers
- Model: DJI 10 inch with 4.7 inch width.
- DJI propellers are designed specifically for High efficiency, Stabilty, and low noise.
- The 10 inch is the diameter of the propeller.
- 4.7 inch is the pitch of the propeller.
- The size of the propeller is kept large to maintain weight-to-thrust ratio.
3.Battery
- Model: LiPo 2200mAh, 80/120c.
- The Lipo indicates the Lithium polymer battery is used which has properties like light weight, more discharge rate, and high current density.
- It can discharge 2.2 A per hour.
- The notation 80/120 c indicates the capacity rate to discharge.
- 80 c is the continous discharge rate and 120 c is the brust discharge rate which last's only for few sec and it is the maximum discharge rate.
- 6 cell Ni-metal hydride battery is equal to 2 cell Lipo battery.

Data Sheet of Battery

4.ESC(Electronic speed controller)
- Model: Max 20A.
- It can handel high current, making it suitable for high power application.
- It is 20% more than the maximum current drawn by the motor to satishify the condition.

5.Frame
-
Material: Carbon fiber (weight: 200 grams).
-
Lightweight and durable, enhancing stability and endurance.
6.Flight Controlers
- Sensor Fusion
combining data from multiple sensors
Manual Calculations :
Thrust :

Outcomes from eCalc:
1.Thrust-to-weight ratio:
Achieved: 3:1
To ensure stable flight at playload 1376 g
2.Hover flight time:
Achieved: 13.5 min
3.Mixed flight time:
Achieved: 7.7 min
4.Total weight:
Achieved: All up weight is 850 g
5.Maximum Speed:
Achieved: 61 Kmph
6.Efficiency at hover:
Achieved: 73.3 %
7.Estimated temeprature of motor:
Achieved: 31°C
Analysis
Component compatibility
The motor, ESC, and propellers are well-matched, as evidenced by the efficiency and stable RPM performance. The selected battery complements the overall design, allowing sustained operation without overheating.
Table of specification
| Sl. No. | Component Name | Specification | Datasheet Link | Cost (INR/USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Motor | Ecoll 2814-830 (830 KV) | View Datasheet | $ 22.9 |
| 2 | Propellers | DJI 1047 | View Datasheet | $ 4.5 |
| 3 | Battery | LiPo 2200mAh, 80/120C | View Datasheet | $ 41.39 |
| 4 | ESC (Speed Controller) | Max 20A | View Datasheet | $ 12 |



Task 2: Regulations
Objective:
To learn about ICAO, SARPS, QCI, BIS, stakeholders, BVLOS, and their basic laws.
Outcomes&Learning:
ICAO : International Civil Aviation Organization
ICAO is a United Nations agency that helps countries cooperate in the field of civil aviation, promoting safe, efficient, and sustainable air travel.

DGCA : Directorate General of civil Aviation
Directorate General of civil Aviation comes under Civil Aviation Ministry which handles the Aviation Sector of India and ensures the procedure is going on within the legal entities.

It maintains Digital Sky Platform of India which issues license to various Unmanned aircraft and creates the Red, Yellow and Green Zones
Red Zone:
It includes areas where drone operations are strictly prohibited unless explicitly permitted by the Central Government.
Yellow Zone:
The specified airspace over Indian territorial waters and land areas that is off-limits to unmanned aircraft system operations and requires authorization from the relevant air traffic control authority.
Green Zone:
It encompasses airspace up to 400 feet and areas within 8-12 km from the perimeter of an operational airport up to 200 feet.

Drone Rules 2021
Drone Rules which are enclosed in the Gazette of India which are approved by the civil aviation ministry government of India.

QCI : Quality Council of India
The Quality Council of India (QCI) plays a significant role in civil aviation by promoting quality, safety, and efficiency in various aspects of the aviation sector.

BIS : Bureau of Indian Standards
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) plays a crucial role in civil aviation by ensuring quality, safety, and reliability in aviation-related products, infrastructure, and operations.

BVLOS(Beyond visual line of sight)
Objective: To understand the before flying procedure, and flying procedure of the BVLOS
- SOP : Standard operating procedures should be submitted to DGCA.
- Security clearances : Need clearances from the Ministry of home affairs(MHA) to fly BVLOS.
- Flight height rules : 400 feet above ground level is allowed and if we want to increase the height we required permission from the AAI.
- Condition for energy reserve : 15% energy should be left when finishing the mission to cope up with emergency like situations.
- Risk assessment : Training team members in Hazardous identification and risk management situations like collisions with other aircraft, obstacles, or people, weather conditions, or equipment malfunctions.
- Qualification of pilots : Drone pilots should have valid certificates.
- Approvals : To fly BVLOS we need approvals from the Ministry of defense and local authorities.
- Single point Control : Appointing a person in the ATC office to communicate during the flight.
- Plans of flight : Require flight information center number and Air defense clearance number.
- NOTAM : Issue a notice to other air service agencies to inform about our flight.
- Time to fly : We can fly in day time only and there must be good weather while launch and landing.
- Drone Requirements :
- Micro or small category.
- Should have valid Drone Acknowledgement Number.
- Good battery life for long duration flights.
- Should weather resistant.
- Contain real time tracking devices.
- Must have barometric sensor for accurate altitude.
TASK 3: Introduction to Aerodynamics and Aircraft Structures
Objective :
- Study Bernoulli’s Principle, Newton’s Third Law in aviation, and aerodynamic forces.
- Understand lift, drag, thrust, weight, and stability.
- Learn about primary and secondary control surfaces.
Outcomes&Learning :
Bernoulli's Principle
Bernoulli's Principle states that an increase in fluid (like air) velocity is accompanied by a decrease in its pressure, and vice versa.
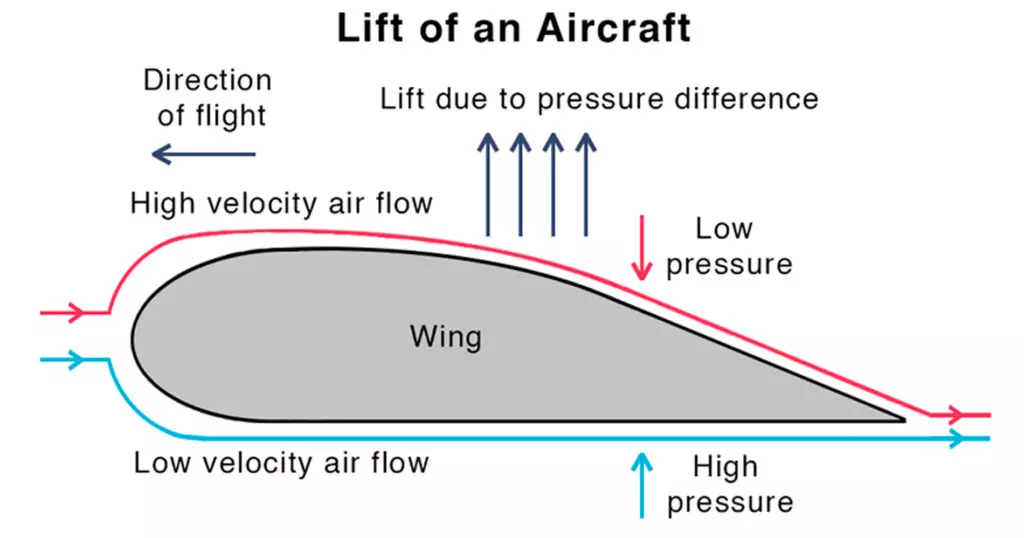
Newton's Third Law of Motion
Every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.

Lift Equation


Flight Control Surfaces
Primary Control Surfaces

Secondary Control Surfaces

TASK 4: Different Flight modes in Mission Planner
Objective : To be familiar with the various flight modes available in the Mission Planner software and understand their use cases.
Outcomes&Learning : Learnt about different flight modes available in the mission planner
-
Stabilize Mode
Manual control with auto-leveling.
Pilot controls throttle to maintain altitude.
Great for basic manual flying. -
Altitude Hold (AltHold)
Maintains current altitude using a barometer.
Manual pitch, roll, and yaw control.
Good for hovering and learning. -
Loiter Mode
GPS-based position hold (holds position and altitude).
Very stable; great for photography and safe hovering. -
PosHold (Position Hold)
Similar to Loiter but more responsive to stick inputs.
Good balance between control and automation. -
Auto Mode
Executes a pre-planned mission with GPS waypoints.
Fully autonomous flight. -
RTL (Return to Launch)
Returns to the launch point automatically.
Triggered manually or on failsafe (e.g., low battery, signal loss). -
Guided Mode
Controlled via ground station (click on map to send drone).
Useful for interactive mission control. -
Circle Mode
Drone flies in a circular path around a set point.
Can adjust radius and speed. -
Drift Mode
For FPV-style flying.
Yaw is controlled automatically; feels like flying a plane. -
Sport Mode
Manual mode with angle limits and rate control.
Faster and more agile; similar to Stabilize but more dynamic. -
Brake Mode
Instantly halts the drone and holds position (requires GPS).
Emergency "pause" function. -
Follow Me Mode
Follows GPS location of a ground control device (like a laptop/tablet).
Used for tracking moving targets. -
AutoTune Mode
Automatically tunes the PID parameters for optimal flight performance.
Requires some flight space and setup. -
Land Mode
Automatically lands the drone in a controlled descent.
Can be triggered at the end of an Auto mission or manually. -
Takeoff Mode
Used in Auto missions to arm and take off to a specified altitude.
Autonomous vertical launch. -
RTL, Smart RTL, and Land
RTL: Simple return to launch.
Smart RTL: Retraces recent flight path back to launch.
Land: Immediate, controlled landing at current location.
TASK 5: Understanding and Designing an Air foil
Objective :
• To Understand the fundamentals of an Aerofoil, terms associated with it, the
nomenclature, concept of turbulence.
• Use Fusion 360 to model an NACA 4412 air foil of 100 mm chord length & 160
mm air foil span, in Fusion 360 using DAT to Spline/Canvas tool.
• Simulate lift and drag at 25 m/s wind speed to ensure at least 5N lift, use
Autodesk CFD for simulation. (Compare with 2 materials, composite based
air-foil & wood based air-foil), and stating the angle of attack in the report.
Outcomes&Learnings :
Nomenclature

Labelled Airfoil

Air Foil :
I Designed air foil at Autodesk
Front view of the airfoil

3-D View of airfoil

click here to view my continued Report
