

TASK 6: RF Communication in UAVs
Objective :
•To Learn about radio frequencies used in UAVs (2.4GHz, 5.8GHz, Lora).
•To Understand the various security implications in the different wireless
protocols used in drones, along with the emerging threats and ways of
mitigation.
•To Understand the procedure which goes behind the binding of an ELRS receiver.
•To Bind the 2.4 GHz RP1 Rx with the TX 16S.
Outcomes and Learnings : \
Radio Frequencies
I learnt about the differences between the 2.4GHz and 5GHz radio frequencies
2.4GHz
- The most common radio frequency and known as single band frequency.
- Most of the devices use 2.4GHz frequency that leads potential signal overlap and congestion.
- Transmits data at a slower speed.
- It has long range.
- It can penetrate solid objects better.
- Among 11 channels it has only 3 non-overlapping channels.

5 GHz
- The radio frequency also known as double band frequency.
- Few devices use 5GHz radio frequency it is less crowded.
- Transmits data at higher speed.
- It has short range.
- Harder to penetrating solid objects.
- It has 24 non-overlapping channels.

LORAWAN
- Long Range Wide Area Network.
- LORAWAN uses an unlicensed frequency band for long-range communication.
- It can be used for a range of 3 miles in urban area and 10 miles in rural area.
- LORAWAN devices can have battery life of more than 12 years because it operates at low power and low bandwidth.
LoRaWAN Devices
Class A
- Longest battery life.
- Stays in the sleeping mode majority of the time.
- It is bi-directional communication device.
- It can response to the messages(Downlink) only if it sent the messages(uplink).
Ex:- Fire alarm, Flood detector, etc.
Class B
- Average battery life.
- Listens to network periodically.
- It can receive messages (down link) even if it has not sent messages. Ex:- Metering of temp, Humidity, etc.
Class C
- Lowest battery life.
- Listens to the network continuously.
- It has min latency for messages (downlink and uplink) Ex:- Traffic monitoring
LoRaWAN Architecture
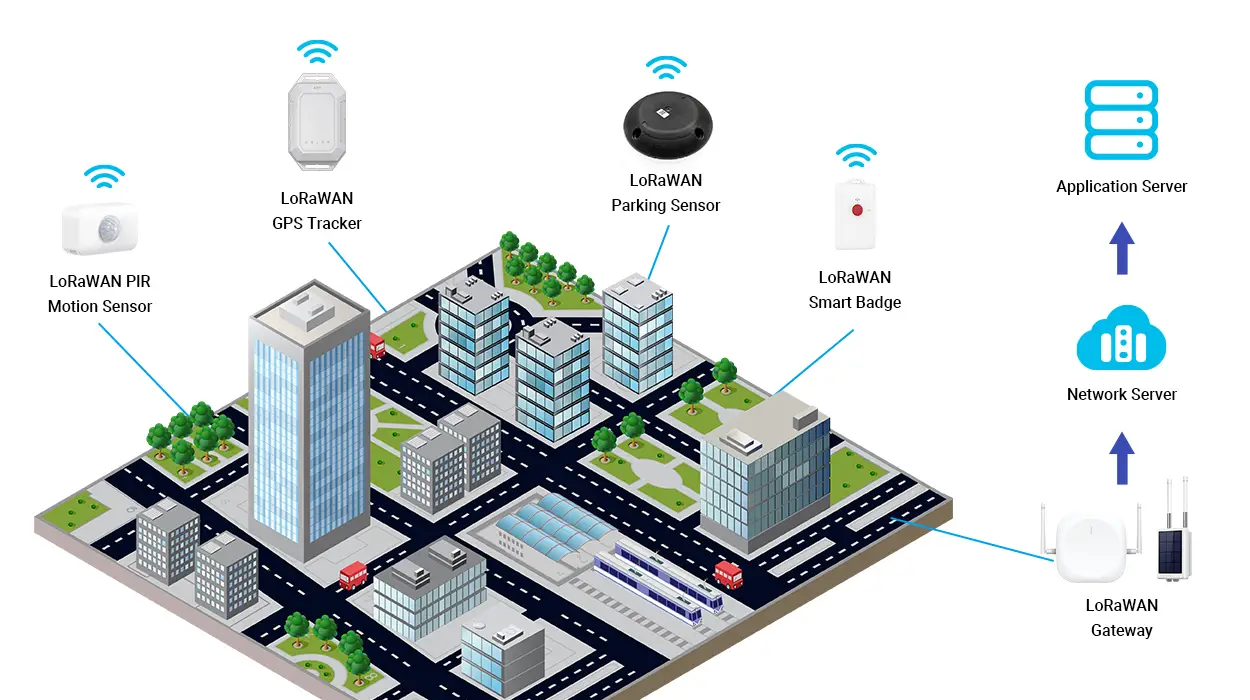
LoRaWAN Components

LoRaWAN Application
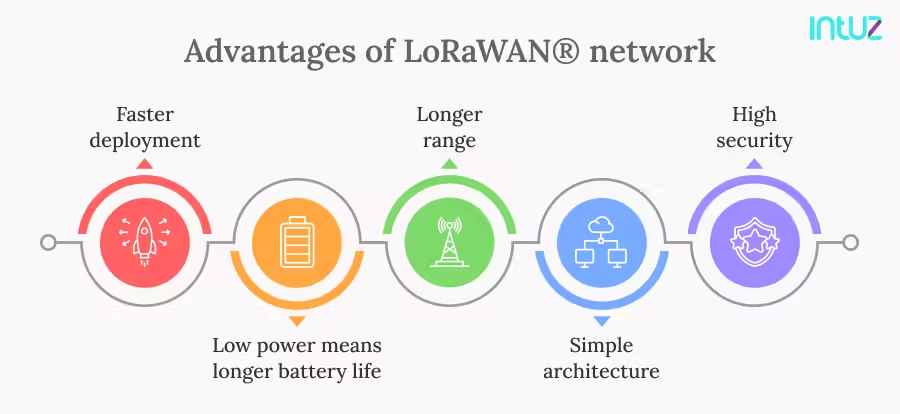
LoRaWAN Advantages
ELRS
ELRS is the High-performance radio control (RC) link designed for first-person view (FPV) drones and other remote-controlled devices.
ELRS VS CROSSFIRE
 ELRS
ELRS
Pros:
- It is open source and mostly used for FPV(first person view) drones.
- ExpressLRS is more affordable than Crossfire.
- Low latency (Transmitter can send messages to the receiver 1000 times per sec) i.e maximum update rate is 1000Hz.
cons:
- ExpressLRS is somewhat more technically complex than other RC systems.
- ELRS communication isn’t secured and isn’t jam resistant.
- ELRS supports up to 12 channels due to limited bandwidth.
CROSSFIRE
Pros:
- The setup process is straightforward.
- Crossfire has been around for years and has proven itself to be reliable and efficient in long-range flights.
- Crossfire offers extensive telemetry features, providing pilots with real-time information about their drone’s status and radio link health.
cons:
- Crossfire is more expensive than ExpressLRS.
- Crossfire has a maximum update rate of 150Hz.
TASK 7: Advanced Flight Control & Tuning
Objective :
• To Understand PID tuning for stability in UAVs.\
• To Learn how GPS hold and altitude hold work in flight controllers, and tabulate
the differences between the two.
• To Make a self-balancing car which balances itself on the principles of PID
control.
Outcomes&Learnings: \
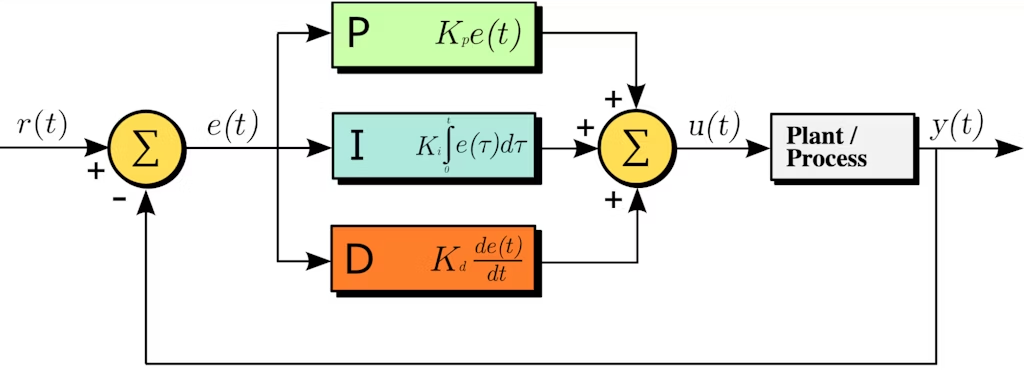
PID(Proportional-Integral-Derivative)


HOLDING
A predetermined maneuver which keeps an aircraft within a specified airspace while awaiting further clearance.
HOLDING PROCEDURE

GPS holding and altitude holding are some of the types of the holding in the aviation
GPS HOLDING
A holding pattern that utilizes GPS navigation to maintain the aircraft's position at a specific way point
- Not stable in the wind turbulence conditions.

ALTITUDE HOLD
The throttle is automatically controlled to maintain the current altitude.
- Stable in the wind turbulence conditions.

TASK 8: Understand about ESC(Electronic speed control)
Objective : To control the speed of a BLDC motor using Arduino UNO, ESC, and a potentiometer.
Outcomes&Learning : I learnt to control the speed of the BLDC motor using Arduino UNO, ESC, and a potentiometer.
Circuit Diagram

Code to Run the motor

Principle of BLDC motor
 Description of components
Description of components
- Arduino Uno : A microcontroller generate the 50Hz PWM signal and depending on pulses width or the high state duration which should vary from 1 millisecond to 2 milliseconds, the ESC will drive the motor from minimum to maximum RPM.

- BLDC Motor : I used 1000 kv motor for performing the task.

-
ESC(Electronics speed controller) : ESC Drives the motor from minimum to maximum rpm

-
Potentiometer : Act as voltage divider by varing the resistances.

Pictures While performing in the lab


TASK 9: Propeller Blade Design & Simulation
Objective :
To understand propeller fundamentals and simulate its aerodynamic
performance.
Outcomes&Learnings :
Basics of propeller :
 Real life application of Diameter and Pitch :
Real life application of Diameter and Pitch :

 2 Vs 3 Blade propellers :
2 Vs 3 Blade propellers :

 Conversion Between 2 blade and 3 blade propeller :
Conversion Between 2 blade and 3 blade propeller :

 Propeller Specifications for the Racing Drone :
Propeller Specifications for the Racing Drone :

 I have designed a propeller in fusion 360
I have designed a propeller in fusion 360


Dimensions of the propeller
All dimensions are in mm
