Yashaswini's Level 2 Report
2 / 9 / 2025
Task 1 : Wireshark
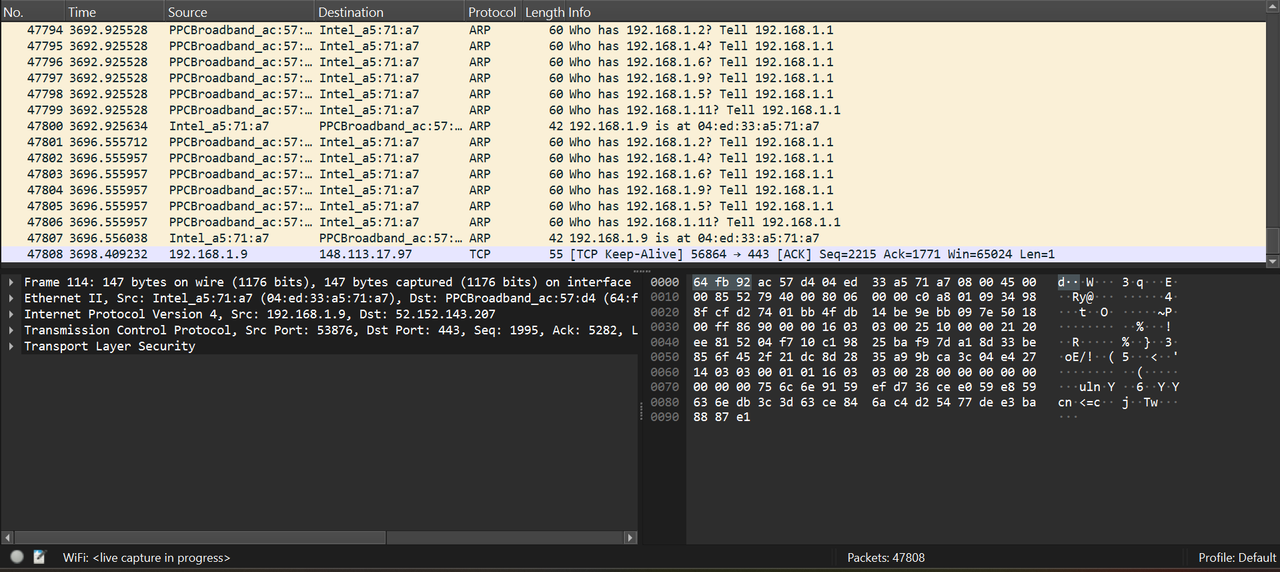
Wireshark is a free and open-source network protocol analyzer. It captures live network traffic and displays it in detail, showing each packet’s source, destination, protocol, and contents. Users can apply filters to focus on specific traffic.
The interface has three parts:
- Packet List (all captured packets)
- Packet Details (layered breakdown: Ethernet → IP → TCP/UDP → Application),
- Hex Dump (raw data).
It is widely used for troubleshooting networks, analyzing security issues, debugging applications, and learning networking concepts.
Filters in Wireshark are used to narrow down network traffic from thousands of packets to only the ones that matter. They make analysis faster and more focused by isolating specific protocols, IP addresses, or ports.
There are two types of filters. They are :
- Capture Filters : They are applied before capturing the traffic. This is done when a specific type of protocol is to be captured and analyzed. This also helps in capturing the required packets in the traffic, reducing the file size.
- Display Filters : They are applied after the packets are captured. This allows focusing on specifc protocols, addresses, or ports in the capture window.
I've used Display Filter in my task to analyze the packets already captured from the traffic. Few filters are given below:
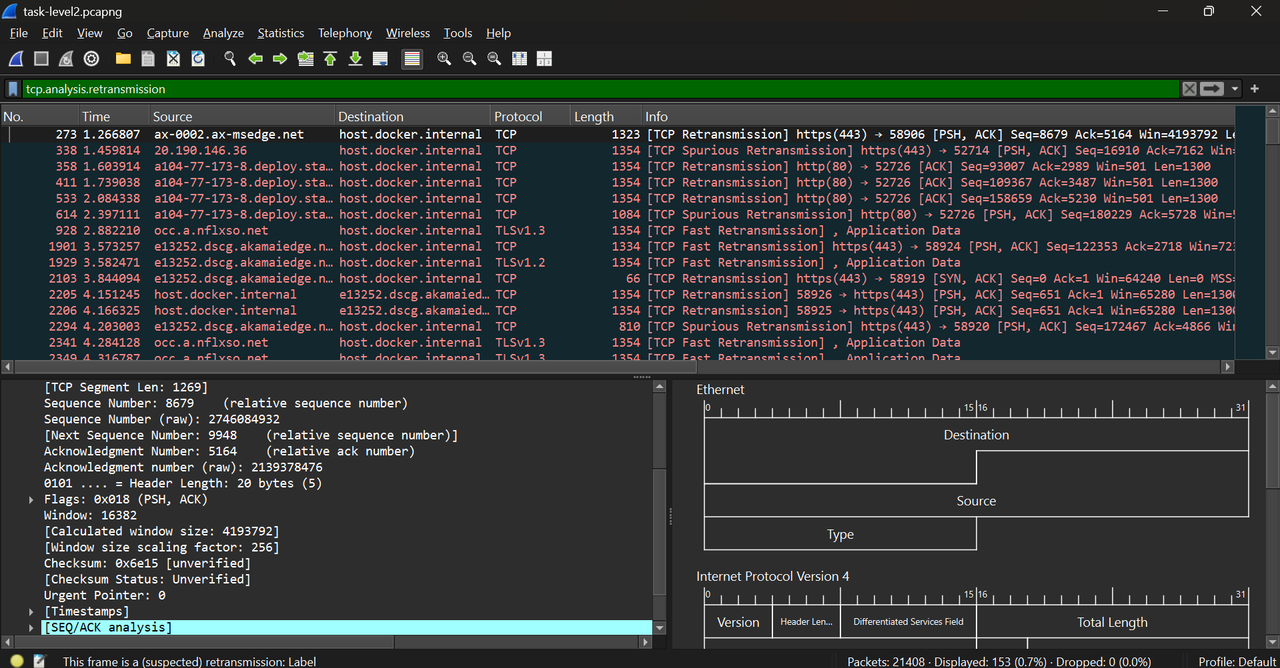
- tcp.analysis.retransmission : This flag appears in Wireshark when a TCP segment (packet) is resent because the sender did not receive an acknowledgment (ACK) from the receiver in time. This usually indicates packet loss, network delay, or congestion. TCP automatically retransmits lost or unacknowledged packets to ensure reliable delivery.
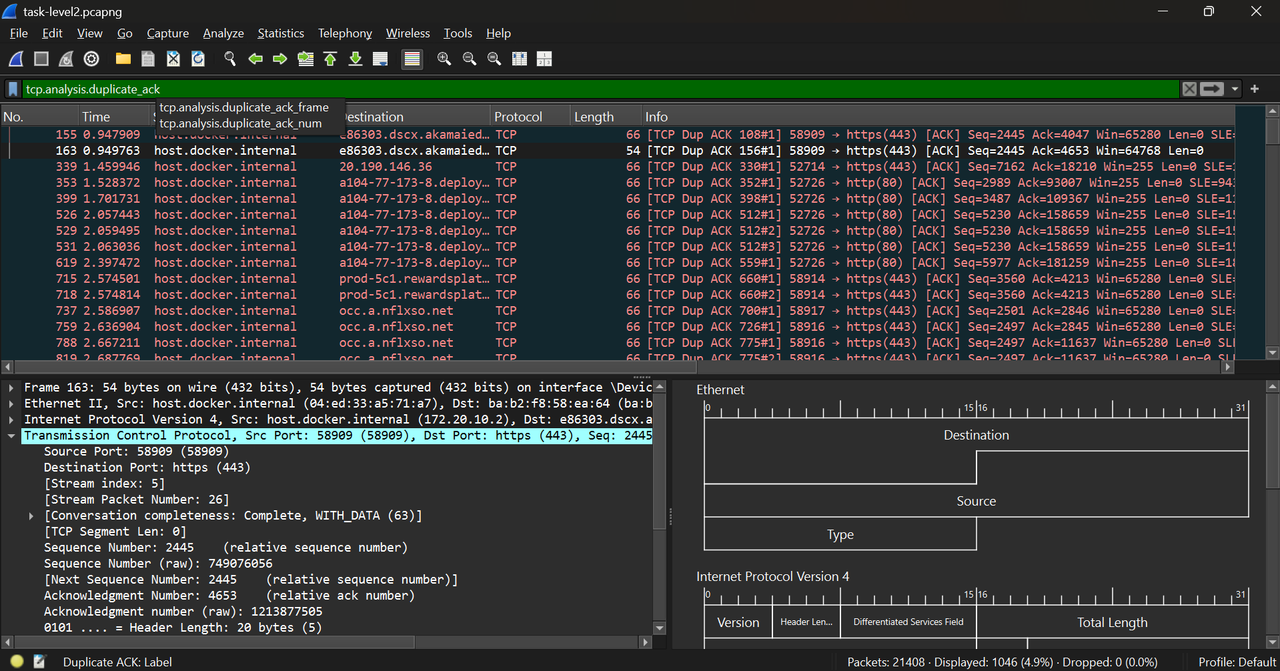
- tcp.analysis.duplicate_ack : It indicates that a TCP receiver has sent a duplicate acknowledgment, meaning it is repeatedly acknowledging the same sequence number because it has not yet received the next expected packet.
- http : It is an application-layer, stateless protocol that enables communication between clients (like web browsers) and servers to exchange resources such as webpages, images, and data.
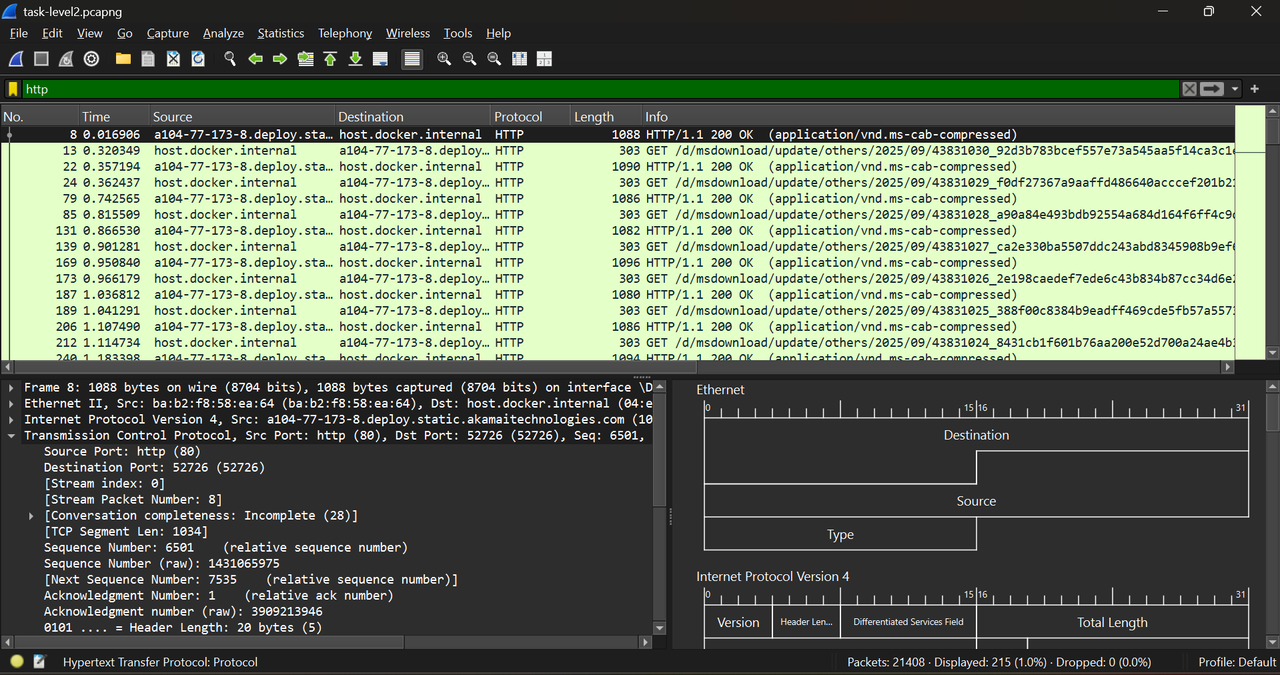
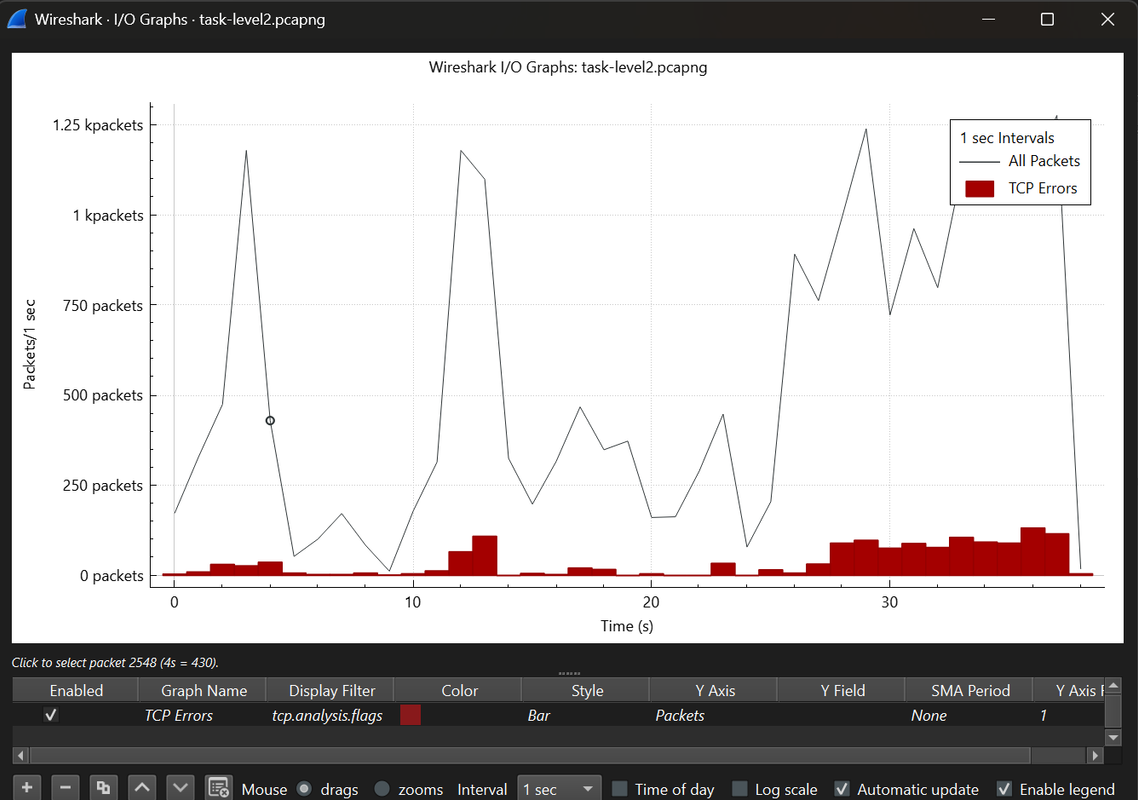
Statistics of the capture time :
Task 2 : Docker
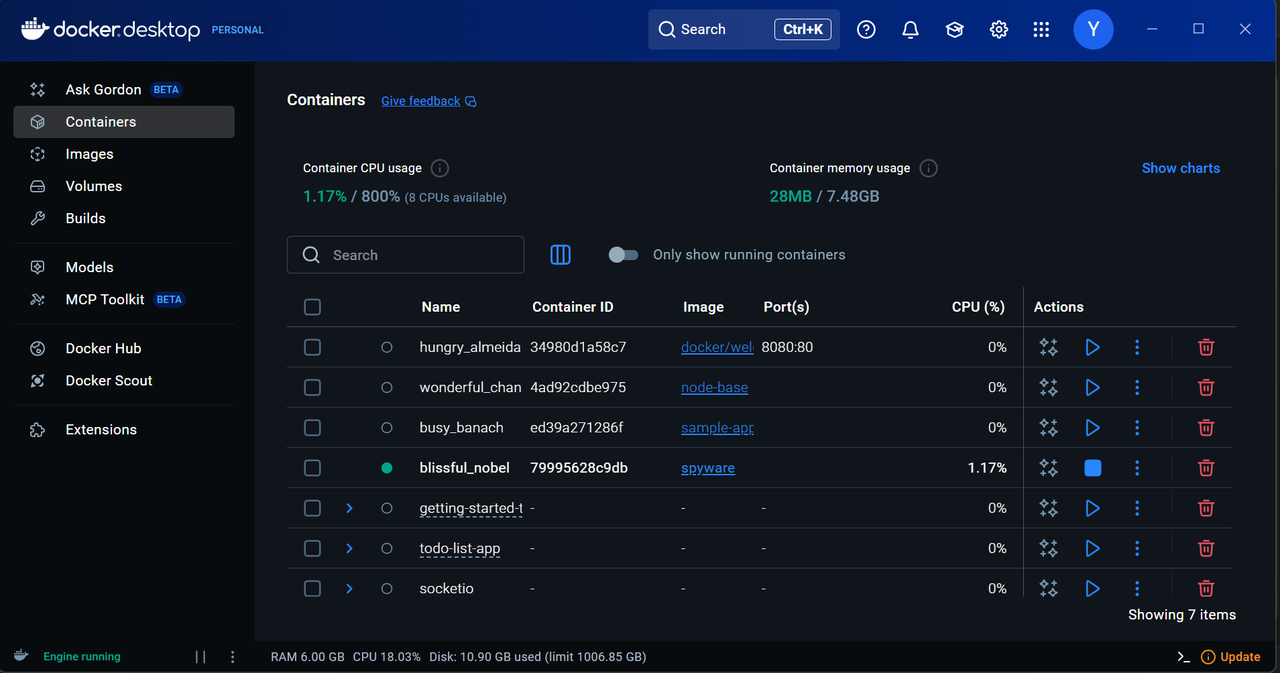
Docker is an open platform for developing, shipping, and running applications. Docker enables you to separate your applications from your infrastructure so you can deliver software quickly. Docker provides the ability to package and run an application in a loosely isolated environment called a container.
Key Components of Docker :
- Docker Engine : It is the core part of the Docker, responsible for running and managing containers. It provides the underlying client–server architecture where the Docker Daemon communicates with the Docker CLI using REST APIs.
- Docker Daemon : It is the background process that usually handles all the heavy lifting tasks like building images, running containers, and managing Docker objects. It listens for Docker API requests from the CLI or remote clients and executes them.
- Docker CLI : The command-line tool that users interact with to issue commands like
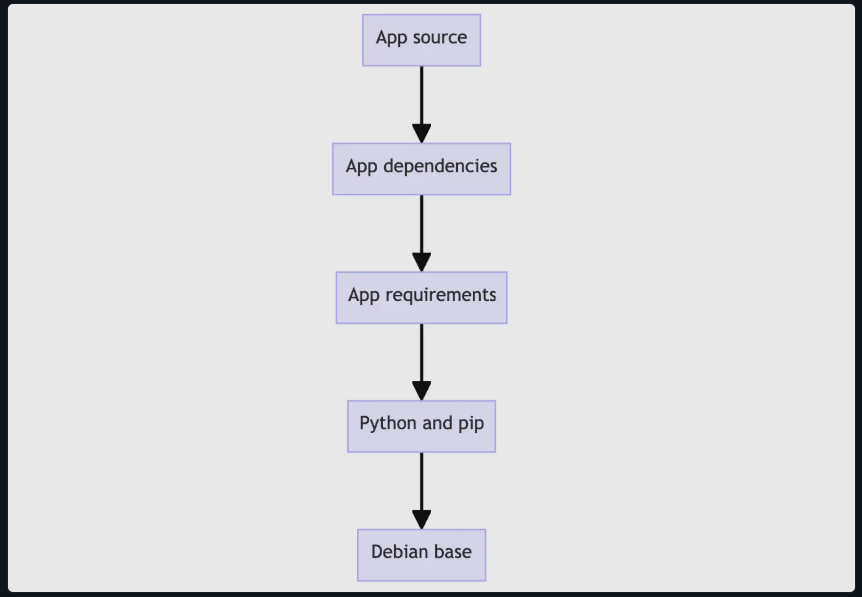
docker run,docker ps, ordocker build. It acts as the user’s interface, sending commands to the Docker Daemon through REST API calls. - Docker Images : Read-only templates that contain everything needed to run an application (code, runtime, libraries, environment variables, config files). Images are versioned and reusable, and you can pull them from registries or build your own using a Dockerfile.
- Docker Containers : Running instances of images that are isolated from the host system but share the host OS kernel, making them lightweight compared to virtual machines. Containers can be started, stopped, moved, or deleted quickly, and multiple containers can run from the same image.
- Docker Hub (registry) : A centralized repository where Docker images are stored and shared. Docker Hub is the default public registry, but private registries can also be used for internal deployments.
- Docker Compose : A tool that allows defining and managing multi-container applications using a single YAML configuration file (
docker-compose.yml). It makes it easier to spin up entire environments (like an app with a web server, database, and cache) with one command.
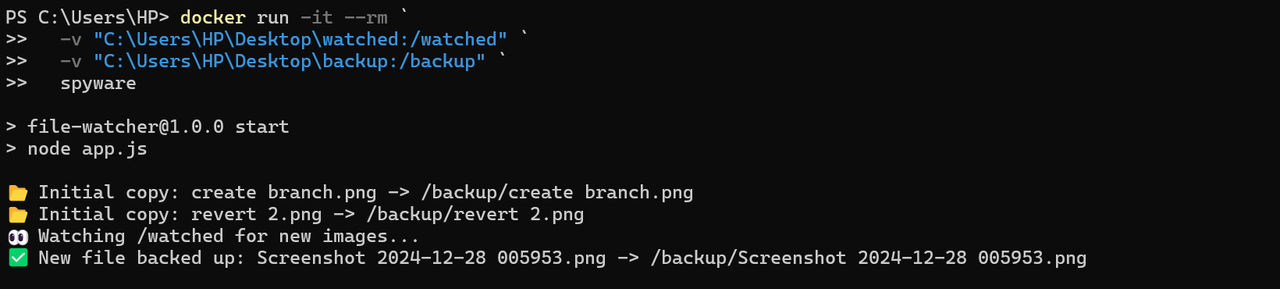
As per the tutorial, I ran the first command using Docker CLI.
docker run -d -p 8080:80 docker/welcome-to-docker
This command helped me run my first container.
I've worked with the example git-file
git clone https://github.com/docker/getting-started-todo-app
given in the tutorial and familiarized myself with the working of Docker by gaining a hands-on experience. During this tutorial, I learnt the role of Dockerfile and YAML file. I made a few modifications to the given getting-started-todo-app and built a new image with the latest tag. I also learnt about the image tagging along with repository creation in Docker Hub and many more.
getting-started-todo-app
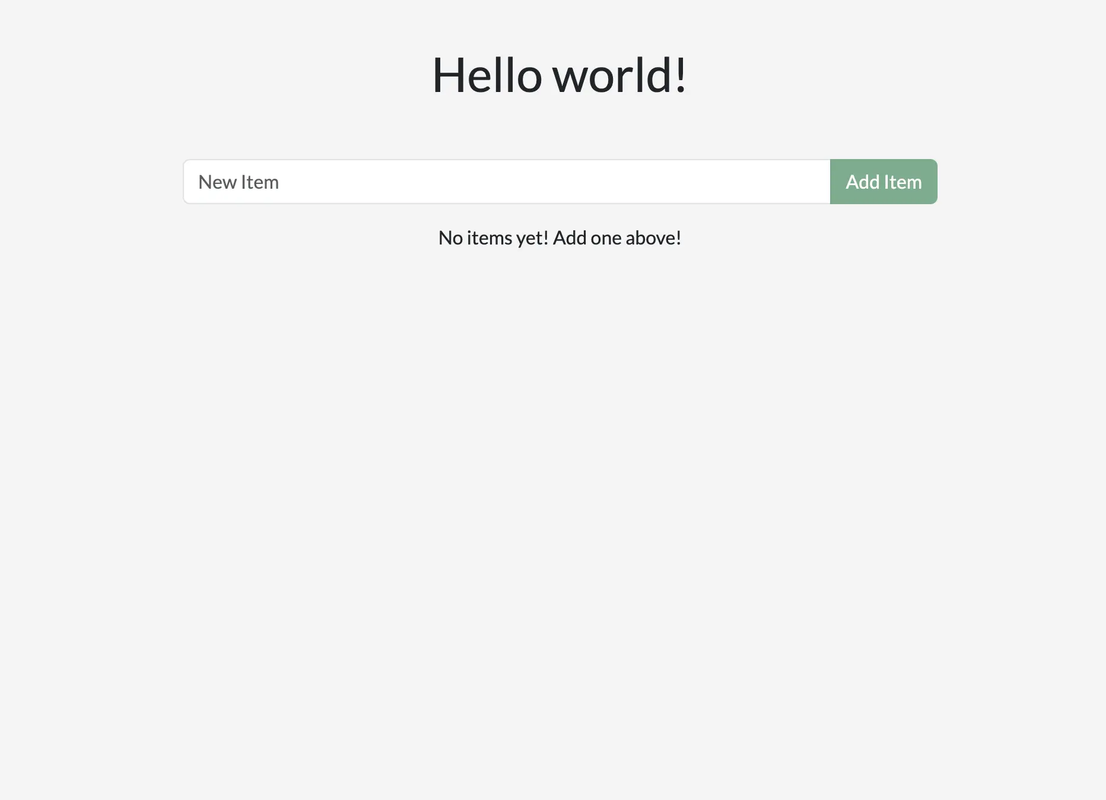
Before modificatons :
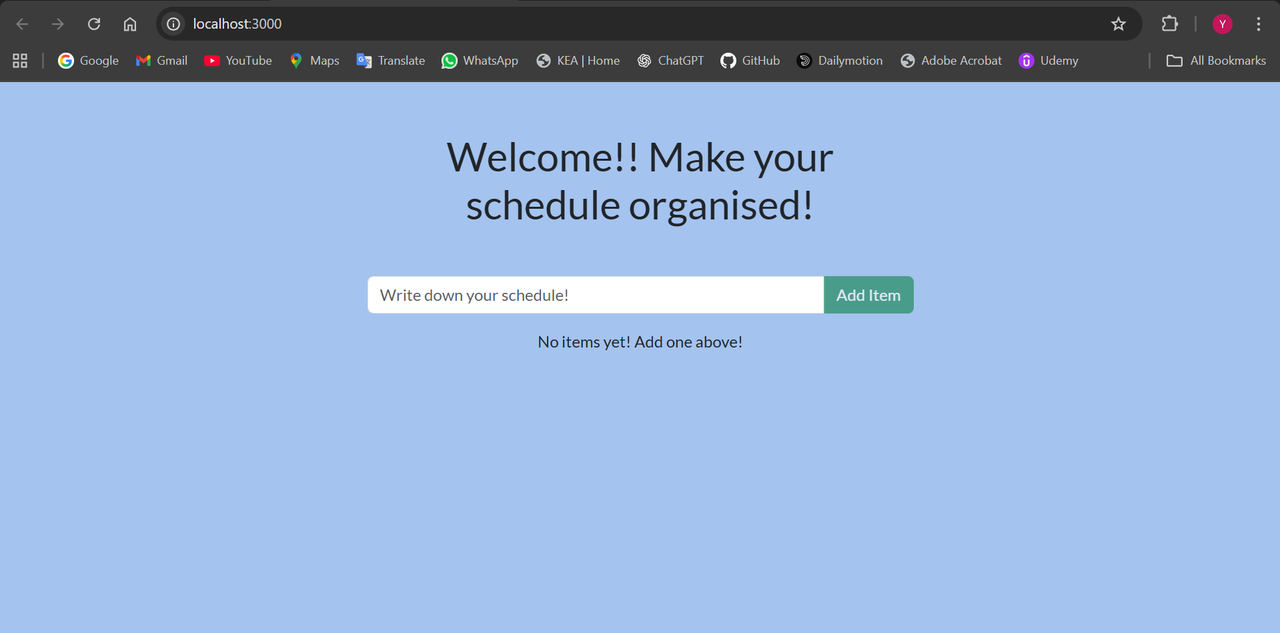
 After modifications :
After modifications :
Task 3 : Docker File Spyware
What is Spyware?
Spyware is a type of malicious software that secretly installs itself on a device to collect information about the user without their knowledge or consent.
Its purpose is to steal data such as browsing habits, login credentials, credit card credentials, or personal files. It runs in background, often unnoticed by the user. It can come bundled with software downloads, email attachments, malicious websites, or ads.
It slows down the system, compromises privacy, and can lead to identity theft or financial loss. It can be prevented using updated antivirus/anti-spyware tools, avoiding suspicious downloads, and by keeping software patched.
I've created a Dockerfile spyware that constantly monitors a folder (watched) and sends all images posted into that folder to another folder(backup) without the knowledge of the watched folder. It was an interesting task to do. I learnt about the spyware by doing a hands-on task.