
COURSEWORK
Asshray's AIR-001 course work. Lv 3
| Asshray Sudhakar | AUTHOR | ACTIVE |

Asshray's Aviation Level 0 Report
23 / 12 / 2024
History of Aviation
Objective:
Explore the theory of aviation and different types of planes. Gain a brief understanding of the history of aviation and the pioneers of the field.
Learning:
Aviation has a history of more than 2000+ years, and it goes like...
References:
All the resource materials specified in the task, no other resources used.
Introduction to Flight Simulators
Objective:
- Use Real Drone Simulator, Learn manual controls and stability handling.
- Get hands-on experience about the motor mixing algorithm.
Learning:
- Connecting & setup of TX16S MK11 TX with the application: It was a pretty easy and straight forward setup as I just had to connect the Tx to my laptop via a USB C cable which came along with the Tx, and then click on, "USB Joystick" on the display of the Tx.
- Understanding the Euler angles (Pitch, Roll & Yaw):

- Channels in a Tx: Channels are controls that are assigned with one single controls each. The TX16S MKII has 16 channels. The most basic Tx would require a minimum of 4 channels i.e. for, Throttle (L), Roll (R), Pitch (R), Yaw (L). If a Tx has > 4 channels, then it means that the Tx can be used for other purposes as well like few servo control, gimbal control, switch control etc. Greater the channels, the more features and controls the Tx offers to the user.
Major Learning:
 In order to change the,
In order to change the,
- Throttle of the drone: All the 4 motors must rotate at a higher speed. Throttle is controlled by moving the left joystick up & down.
- Yaw of the drone: Any one set of diagonal motors (Say 3 & 4) rotate at a higher speed relative to the other diagonal motors (1 & 2), in order for the drone to Yaw. Yaw is controlled by moving the left joystick left & right.
- Pitch of the drone: For forward pitch, the rear motors (2 & 4) rotate faster than the front motors (1 & 3) and for backward pitch its the other way around. Pitch is controlled by moving the right joystick up & down.
- Roll of the drone: For right roll, the left motors (3 & 4) rotate faster than the ones on the right (1 & 4) and for left roll its the other way around. Roll is controlled by moving the right joystick left & right.
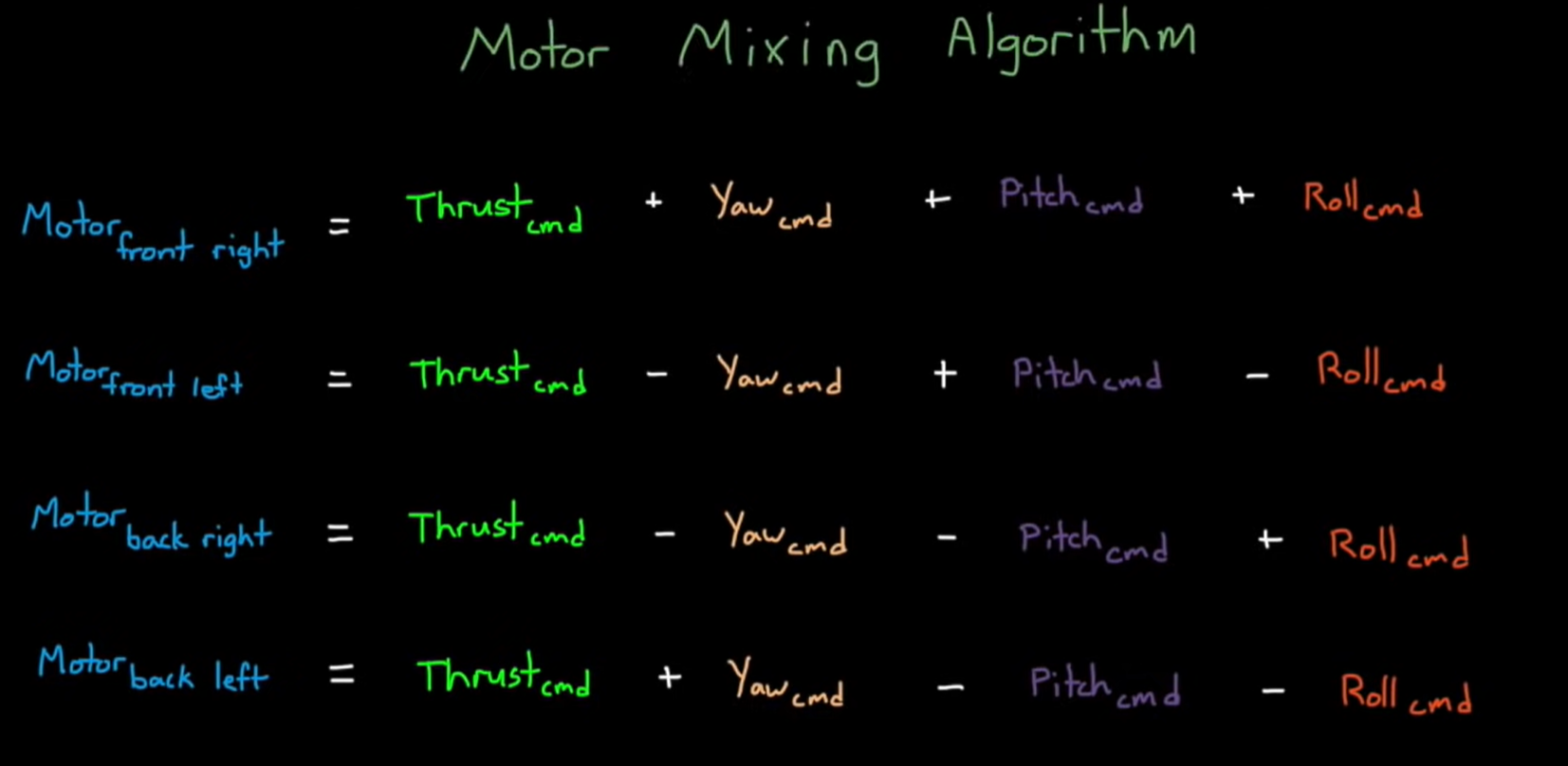
Motor Mixing Algorithm:
Mathematical form of how each of the motor in the drone effects the Euler Angles,
Drone Simulation:
References:
All the resource materials specified in the task, no other resources used.
Flying the Airblock Drone
Objective:
- Write a report about the drone which should include the cost, name of the application used to fly the drone, type of motors used, material of the drone, propellers used, battery details etc.
- Fly the drone in a certain specified path as told by the coordinator, record it and put it up on the report.
Learning:
Airblock : a programmable and constructive drone
Airblock is made of magnetized and modular pieces, extremely easy to assemble and disassemble without any tool. The blocks are made from a light artificial foam - Expanded Polypropylene (EPP) a closed-cell foam known for being lightweight, flexible, durable, and solid. The name of the application used to fly this drone is MakeBlock. The modular block system allows multiple shapes as shown below:
- Drone
- Hovercraft
- Triangle
- Spider

The below image shows the full inner structure of the Airblock Drone:

| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Basic Functions | Rise and fall / Advance and Retreat / Steering / Side Flight / Slight Adjustment / Light Control |
| Advanced Features | Hover / Somersault / Customizable Stunts |
| Forms | Six-axis Aircraft / Hovercraft / DIY |
| Environment to Use | Air / Ground / Water |
| Product Dimensions | Six-axis Aircraft: 235×54 mm, Hovercraft: 335×208×126 mm |
| Material | EPP / PP |
| Flight Speed | 0–2 m/s, Adjustable |
| Flight Time | About 6 Minutes |
| Control Range | 10 Meters |
| Flight Height | 5 Meters |
| Battery Capacity | 7.4 V 700mAh, 5.18 Wh |
| Connection Method | Magnetic Connection |
| Control Method | Makeblock App |
| Communication Method | Bluetooth |
| Sensor | Six-axis Gyroscope / Ultrasonic / Barometer |
| Camera Support | No |
| Programming Support | Graphical Programming |
The following are the things which comes inside the box;

References:
All the resource materials specified in the task, no other resources used.
For other Level 0 tasks Click Here