14 / 1 / 2025
Task: Flying the Airblock Drone
Introduction
The Airblock drone, developed by Makeblock, is a modular and programmable flying robot designed for educational purposes. Its magnetic, modular components allow for quick assembly into various configurations, including a hexacopter drone and a hovercraft. The drone is controlled via the Makeblock App, which offers intuitive interfaces for piloting and programming.
Flight Experience
Under the guidance of a coordinator, I had the opportunity to fly the Airblock drone. The assembly process was straightforward due to its magnetic modular design, enabling quick setup without the need for tools. Once assembled, we connected the drone to the Makeblock App via Bluetooth.
The app's user-friendly interface provided multiple control modes, including a joystick for manual flight and options for executing pre-set aerial stunts like flips and spirals. The drone's lightweight foam construction and enclosed propellers contributed to a safe flying experience, even for beginners.
During the flight session, I learned essential protocols for operating unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), such as:
- Conducting pre-flight checks
- Maintaining line-of-sight
- Ensuring awareness of the surrounding environment
The session also emphasized safety standards, including maintaining a safe distance from people and obstacles and understanding emergency procedures.
Landing the drone was facilitated by the app's intuitive controls, allowing for a smooth descent and touchdown.
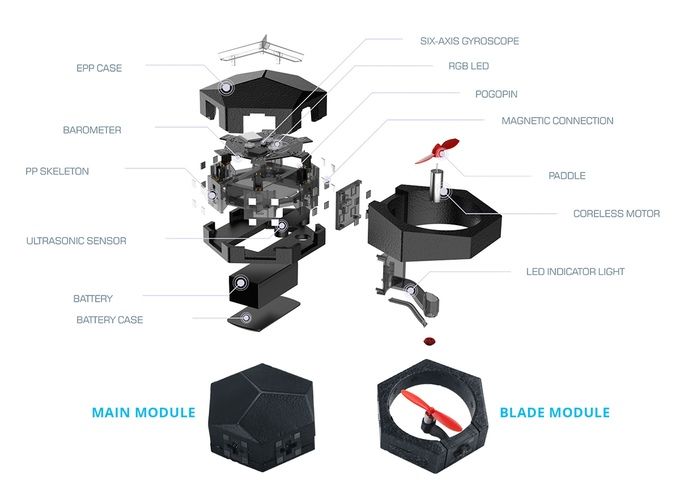
Features of the Airblock Drone
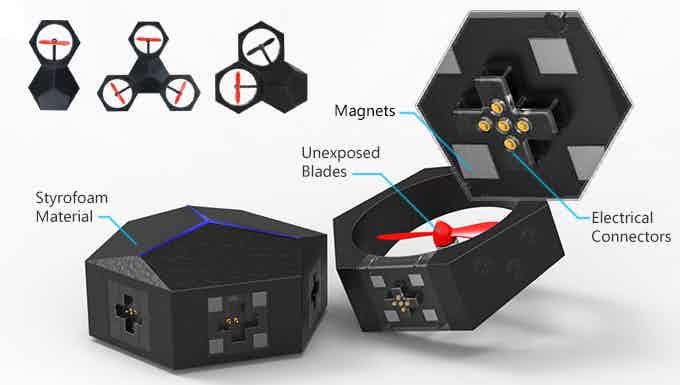
-Modular Design: Comprises one core master module and six power modules that connect magnetically, allowing for various configurations like drones and hovercrafts.
-Durable Construction: Made from lightweight engineered foam, providing durability and safety during flight.
-Programmable: Supports block-based programming through the Makeblock App, enabling users to create custom flight patterns and behaviors. -Safety Features: Enclosed propellers and soft materials reduce the risk of injury, making it suitable for educational environments.
Features of the Makeblock App
-Comprehensive Control: Offers multiple control modes, including pre-set controls and customizable interfaces for different Makeblock robots.
-3D Building Guides: Provides 360° building manuals to assist in assembly, enhancing spatial intelligence.
-Block-Based Programming: Allows users to define custom behaviors and control schemes through an intuitive drag-and-drop interface.
-Multi-Robot Support: Compatible with various Makeblock hardware, including mBot, Ranger, and Airblock.

Conclusion
Flying the Airblock drone was an engaging and educational experience that provided insights into UAV operation, safety protocols, and the principles of aerodynamics. The combination of the drone's modular design and the Makeblock App's versatile features makes it an excellent tool for learning and experimentation.
"Can there exist an aircraft in space without a pair of steel wings."
— Nikhil Parekh
Task: Propeller Design Report
Introduction
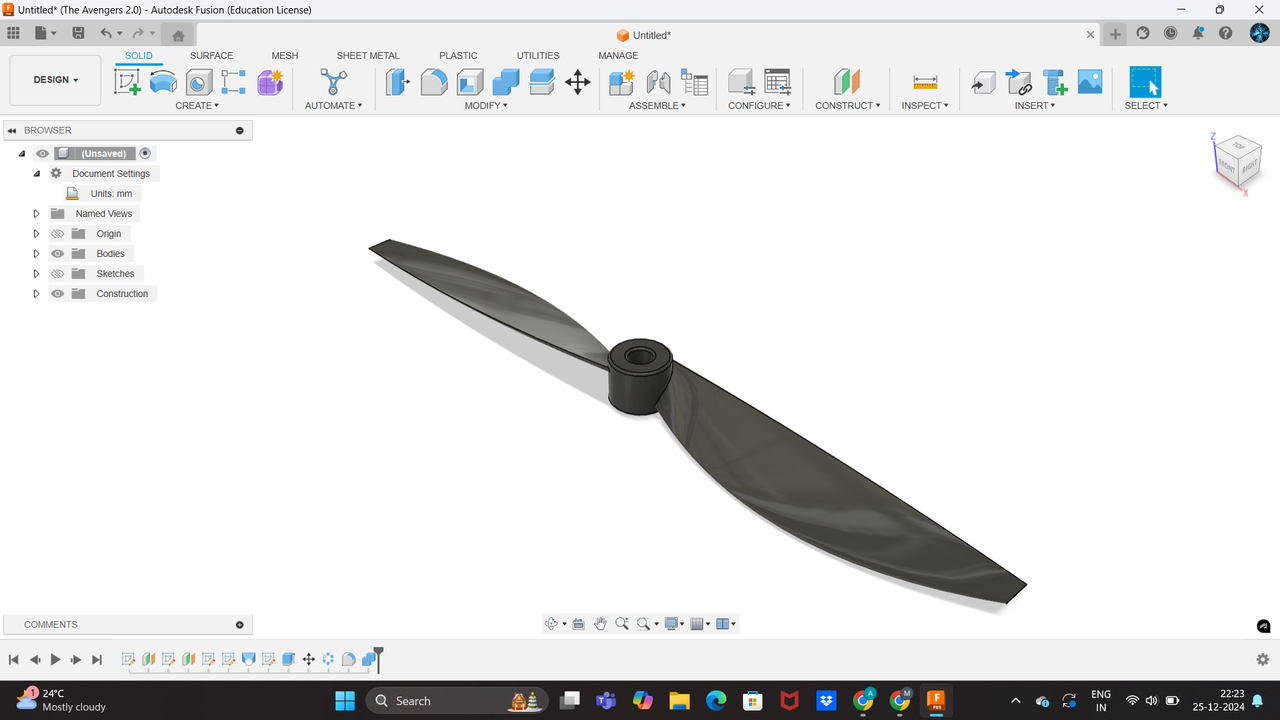
Propellers are essential components in drones, converting rotational motion into thrust to enable flight. For this task, the objective was to design a toroidal propeller capable of generating a lift of approximately 9 Newtons. Both clockwise (CW) and counterclockwise (CCW) propellers were designed to ensure stability and functionality. The propellers were modeled using the Autodesk Fusion 360 .
Drone Propellers
Function and Working
- Purpose: Propellers generate thrust by creating a pressure differential between the top and bottom surfaces of the blade. This allows drones to ascend, descend, and maneuver.
- Mechanics: The rotation of the propeller blades causes airflow. The angle of attack and blade shape dictate how much thrust is produced.
- CW and CCW Propellers: To counteract torque (rotational force), drones use pairs of propellers rotating in opposite directions.
Reading Propellers
- Labeling: Propellers are often marked with dimensions like 5045 (5-inch diameter, 4.5-inch pitch). The pitch refers to how far the propeller would travel in one rotation if it were moving through a solid medium.
- Orientation: CW propellers are mounted on motors rotating clockwise, while CCW propellers are for counterclockwise rotation.
Step-by-Step Process in Fusion 360
Design Workflow
1.Create the Base Profile:
- Open Fusion 360 and start a new design.
- Use the Sketch Tool to draw a 2D profile of the blade’s leading and trailing edges on the X-Y plane.
- Ensure the blade's shape accounts for aerodynamic principles (e.g., a slight camber for lift generation).
2.Generate the Blade Shape:
- Use the Loft Tool to create a 3D blade by connecting the root and tip profiles of the blade.
- Apply a slight twist using the Form Tool to simulate the pitch angle, enhancing airflow efficiency.
3.Design the Hub:
- Create a cylindrical hub using the Revolve Tool. Ensure internal threading matches the motor shaft specifications.
- Include keyholes or flat sections to secure the propeller on the BLDC motor shaft.
4.Replicate for Multiple Blades:
- Use the Circular Pattern Tool to replicate the blade design around the hub, creating a toroidal configuration.
5.Final Adjustments:
- Smooth edges and surfaces using the Fillet Tool to reduce turbulence.
- Check dimensions against required specifications (e.g., Marvel’s dimensions).
Features Used in Fusion 360
- Sketch Tool: For creating 2D profiles.
- Loft Tool: For transforming 2D sketches into 3D geometries.
- Revolve Tool: For creating symmetrical hub components.
- Circular Pattern Tool: For arranging multiple blades around a central axis.
- Fillet Tool: For smoothing sharp edges.
- Parameter Tool: To input and adjust specific dimensions dynamically.
Conclusion
This task provided valuable insights into the design and function of drone propellers. Using Fusion 360, the process of designing CW and CCW toroidal propellers was streamlined, emphasizing both aerodynamic efficiency and practical fit with BLDC motors.
“Aviation is the branch of engineering that is least forgiving of mistakes.” – Freeman Dyson
Task: Assembling a Drone using eCalc
Introduction
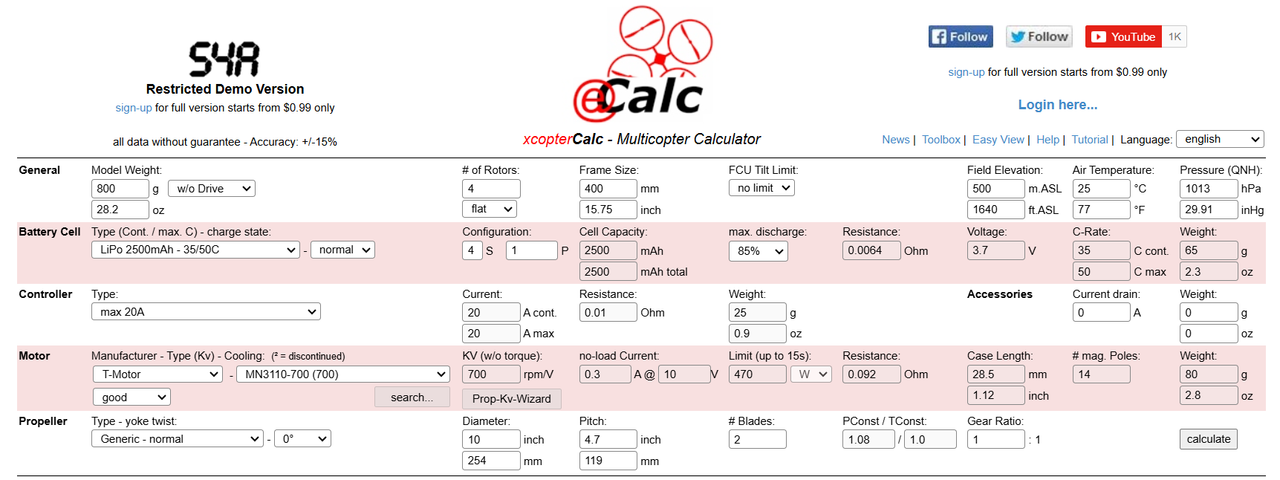
This report documents the design process of a drone with an empty weight of 800 grams using data obtained from eCalc. The aim is to optimize payload capacity, thrust-to-weight ratio, endurance, and overall performance while justifying the selection of materials and components.
Material Selection
For the drone frame, carbon fiber was selected due to its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, rigidity, and resistance to deformation. It ensures the drone remains lightweight (frame weight: 200 grams) while being capable of withstanding mechanical stress during flight. Its non-corrosive properties make it ideal for long-term use in various environments.
Component Selection
1.Motor:
- Model: T-Motor MN3110-700 (700KV)
- Justification: This motor provides a balance between efficiency and power, ensuring sufficient RPMs for stable hover and maneuverability.
2.Propellers:
- Type: Generic 10-inch with a 4.7-inch pitch
- Justification: Optimized for high efficiency and compatibility with the motor, ensuring adequate thrust.
3.Battery:
- Type: LiPo 2500mAh, 4S, 35/50C
- Justification: This battery offers adequate capacity to sustain a hover flight time of 9.5 minutes while maintaining a manageable weight of 260 grams.
4.ESC (Electronic Speed Controller):
- Type: 20A max ESC
- Justification: Matches the current and voltage demands of the selected motor, providing reliable control without overheating.
5.Frame:
- Material: Carbon fiber (weight: 200 grams)
- Justification: Lightweight and durable, enhancing stability and endurance.
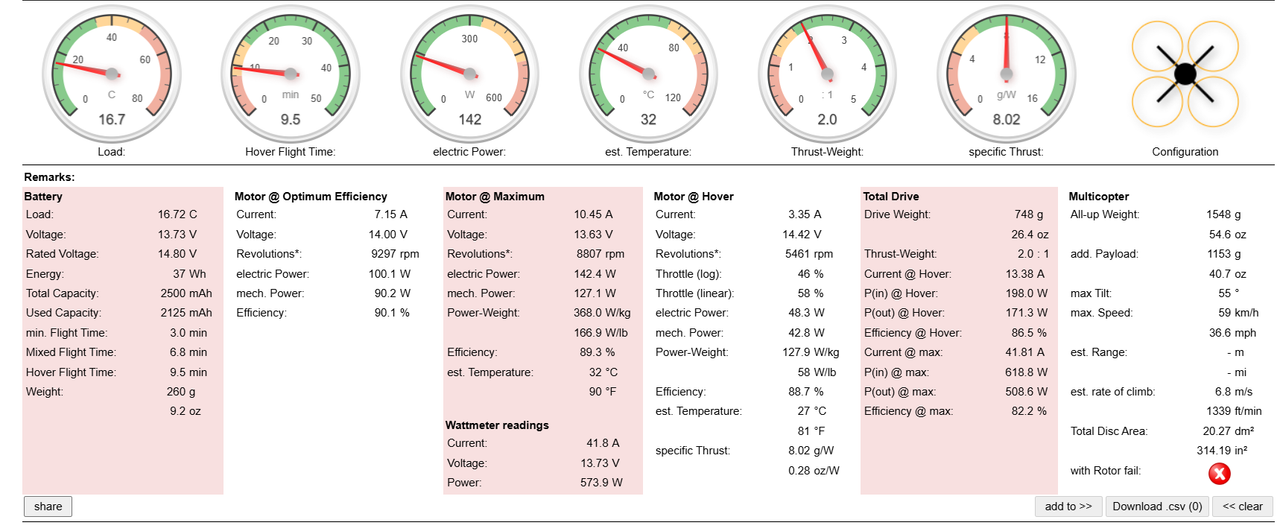
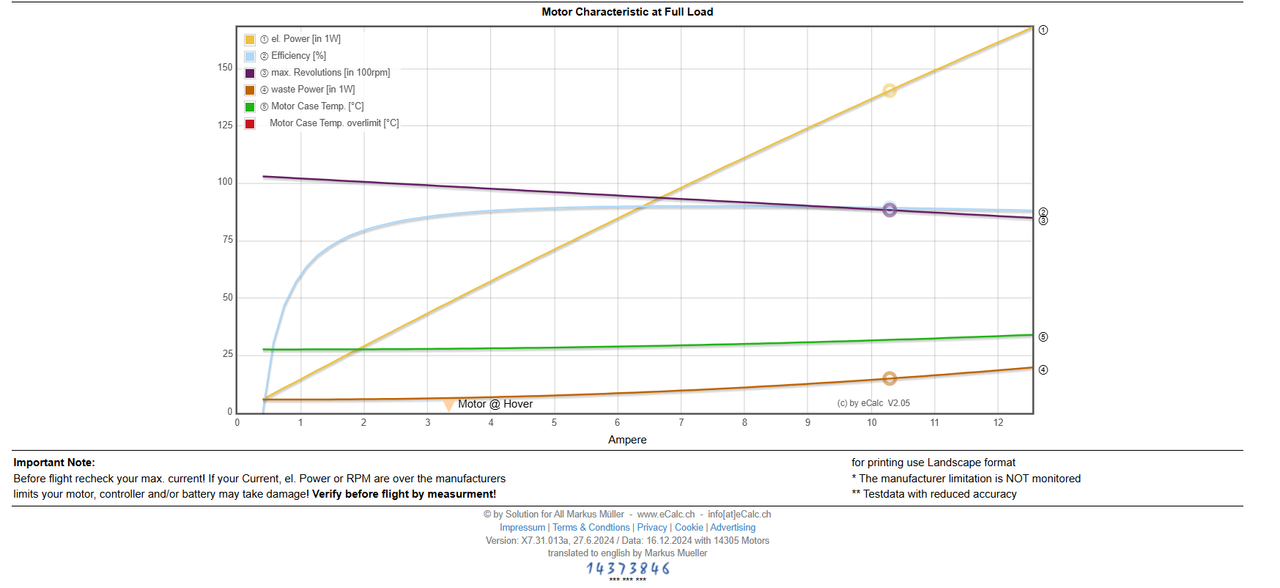
Results from eCalc
Key Performance Metrics
1.Thrust-to-Weight Ratio:
- Achieved: 2:1
- Implication: This ensures stable flight with room for payloads of up to 1153 grams.
2.Hover Flight Time:
- Achieved: 9.5 minutes
3.Mixed Flight Time:
- Achieved: 6.8 minutes
4.Total Weight:
- Frame Weight: 200 grams
- All-Up Weight (including payload): 1548 grams
5.Max Speed:
- Achieved: 59 km/h
6.Efficiency at Hover:
- Achieved: 88.7%
7.Estimated Temperature of Motor:
- At Hover: 27°C
Analysis
Payload and Endurance
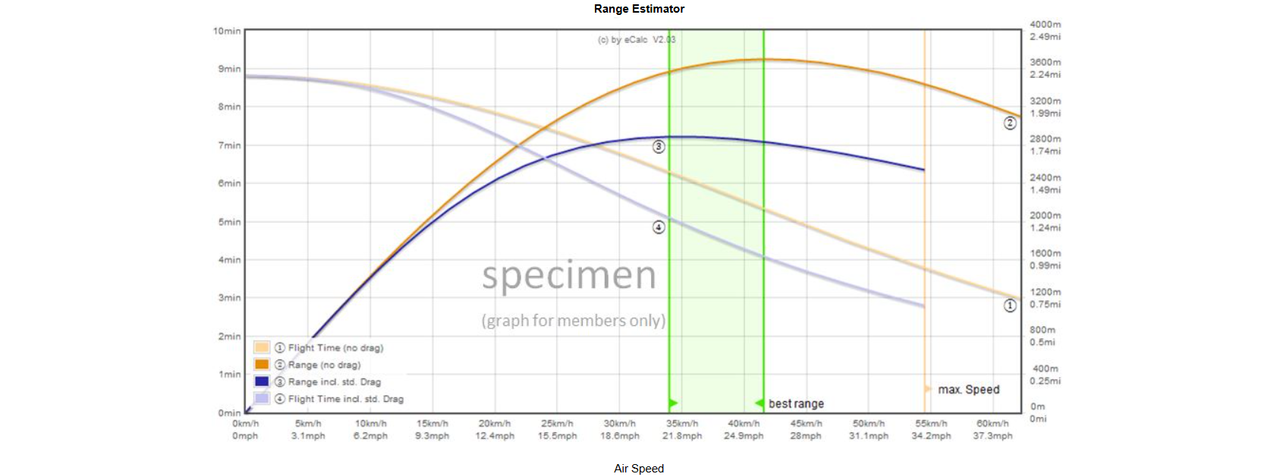
The thrust-to-weight ratio of 2:1 provides ample room for payloads while maintaining stable flight. The hover time of 9.5 minutes is ideal for most mid-range applications, ensuring efficient energy use from the battery.
Component Compatibility
The motor, ESC, and propellers are well-matched, as evidenced by the efficiency and stable RPM performance. The selected battery complements the overall design, allowing sustained operation without overheating.
Takeaways
- The importance of thrust-to-weight ratio in drone design.
- Understanding the balance between weight, power, and endurance.
- Learning to interpret motor and battery datasheets for optimal selection.
- Familiarization with tools like eCalc to simulate performance metrics.
Conclusion
By carefully selecting lightweight yet durable materials and compatible components, the designed drone achieves optimal performance metrics. The process highlights the importance of balancing payload capacity with endurance and efficiency.
“Aviation is poetry. It’s the finest kind of moving around, you know, just as poetry is the finest way of using words” – Jessie Redmon Fauset
Report continued...(https://hub.uvcemarvel.in/article/83e6b984-97d3-45ae-b3f6-c7bf1f57f228)