COURSEWORK
Neeraj's IOT-001 course work. Lv 1
| Neeraj Kumar Gupta | AUTHOR | ACTIVE |

Neeraj's level1 report
9 / 9 / 2025
TASK 2:API
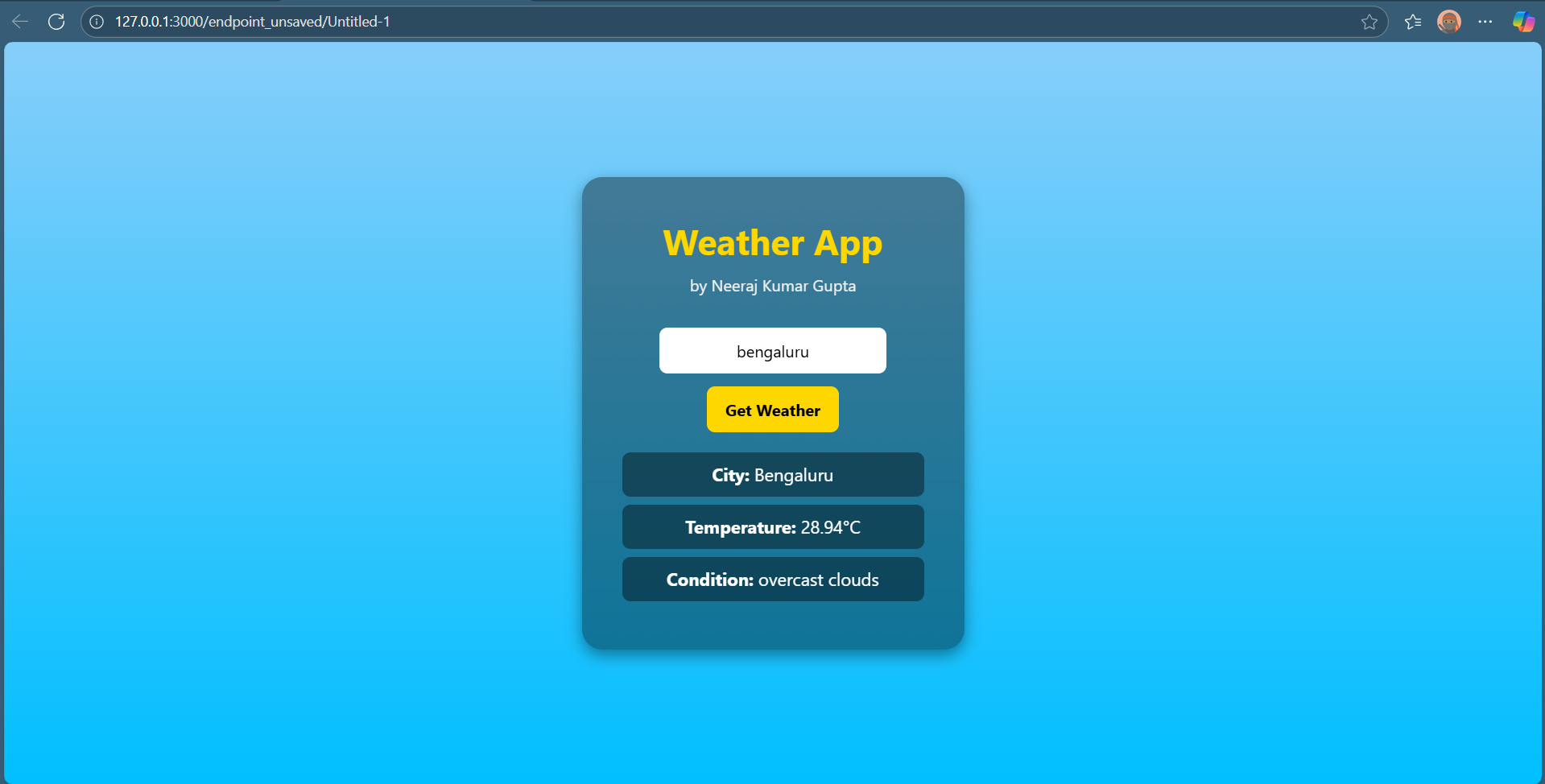
Weather API Integration
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are used to enable communication between two software components through a defined set of rules and protocols. In this task, I created an account on the OpenWeather API and obtained my API key. Using this API, I was able to fetch real-time data on temperature and weather conditions for a specified location. I then built a simple web page that uses this API to display the weather report for Bengaluru.
TASK 3 : WORKING WITH GITHUB
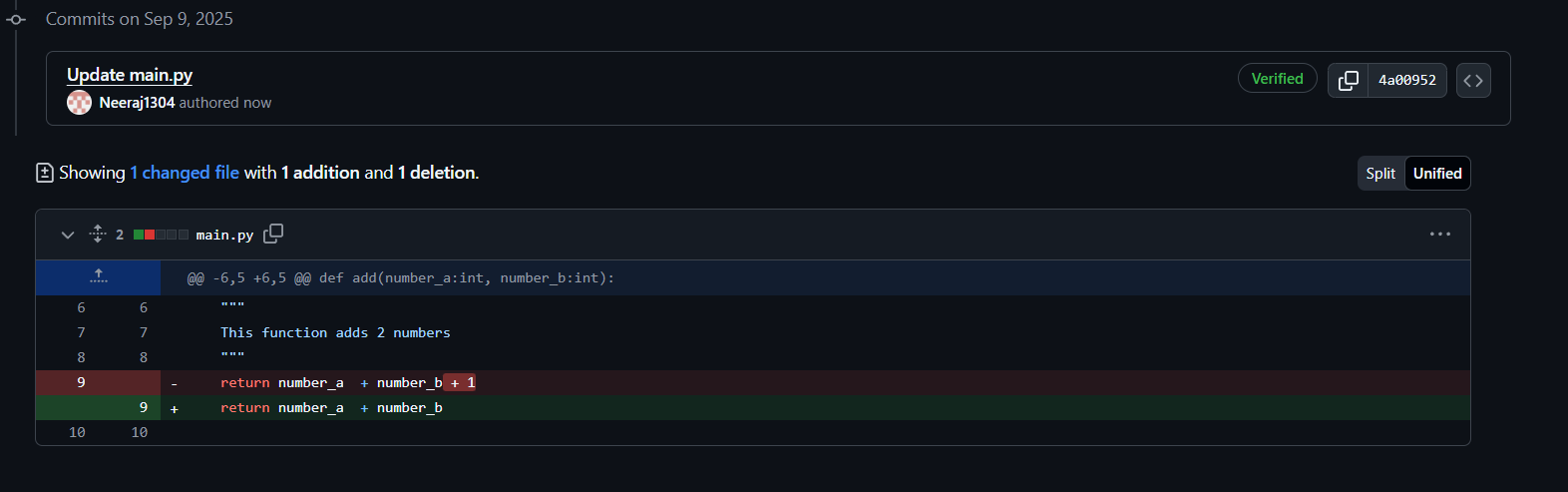
Got familiar with GitHub by learning how to create a repository, make pull requests, and perform other common actions. I successfully completed the tasks mentioned in the README files, including forking a repository, correcting the code, and submitting a pull request.
TASK 4: Get Familiar with the Command Line on Ubuntu and Perform the Following Subtasks
Understood the basic command prompts used in the Ubuntu Linux terminal
- Created a folder named nk using
mkdir nk. - Navigated into the nk folder using
cd nk. - Created a blank file without using any text editor by running
touch blankfile.txt. - Listed the files in the folder using
ls. - Generated 2600 uniquely named folders within the nk directory using:
for i in {1..1300}; do mkdir "M$i" "B$i"; done - Concatenated two text files and displayed the combined content on the terminal using
cat file1.txt file2.txt.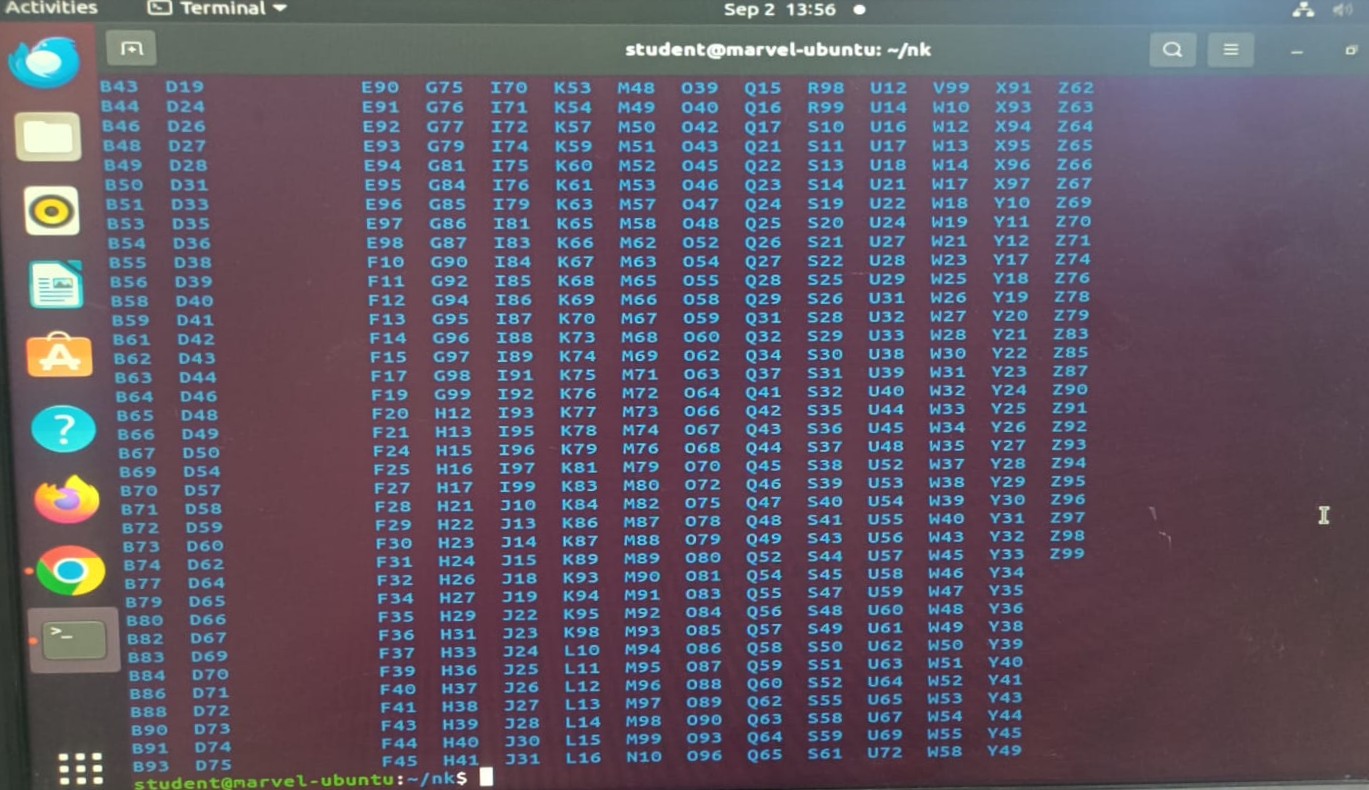
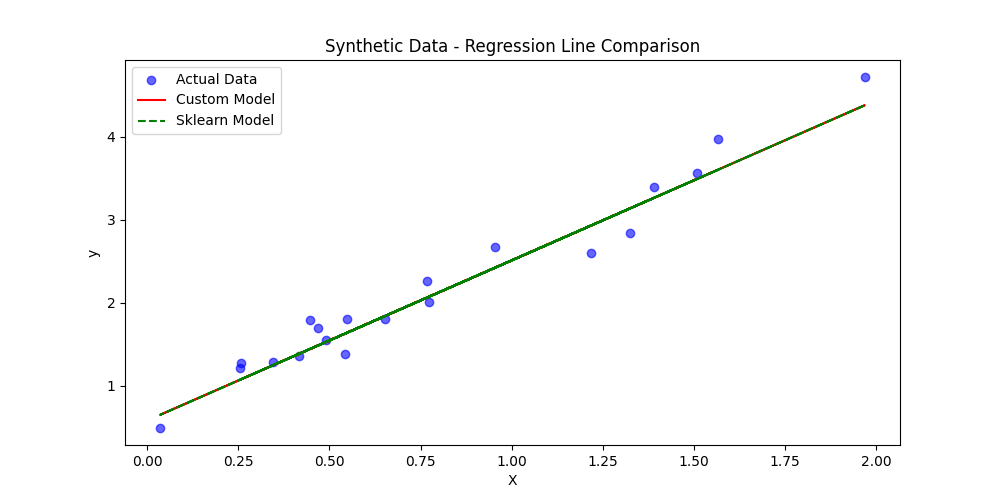
TASK 5: Build Your Own Brain – Linear Regression from Scratch
In this task, I implemented Linear Regression from scratch to understand the core mechanics of machine learning, using the California Housing dataset. The goal was to manually apply gradient descent to optimize weights and minimize prediction error, without relying on any machine learning libraries for training. The process involved feature scaling, proper weight and bias initialization, and careful selection of the learning rate to ensure stable convergence. After training, I compared the performance of my custom model with scikit-learn's LinearRegression, analyzing metrics such as MSE, MAE, and R², and visualizing the line of best fit against the actual data points. This task helped me understand the importance of gradient descent, feature normalization, and model evaluation, while appreciating the convenience and efficiency of inbuilt ML libraries. LINK OF THE CODE
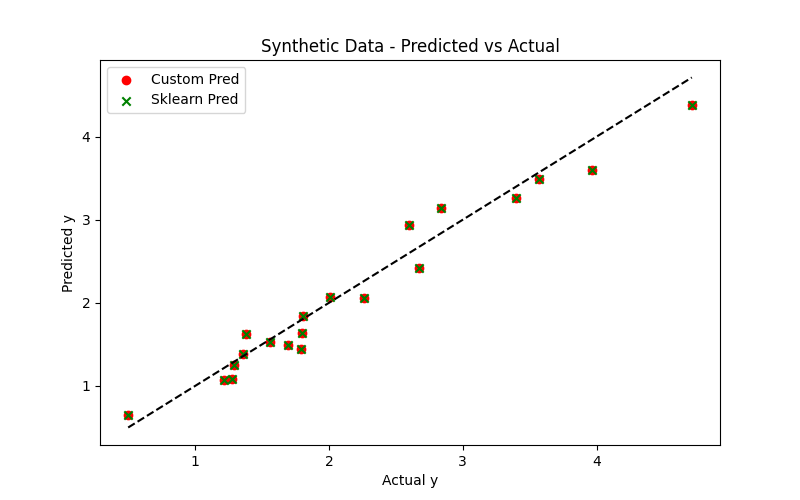
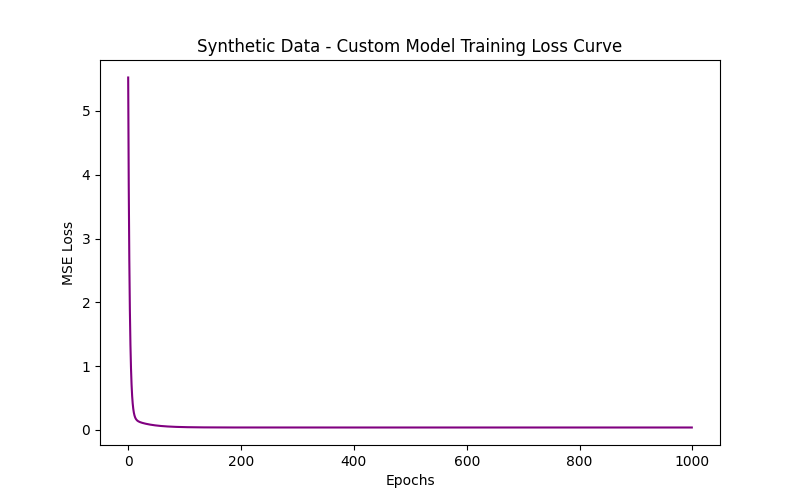
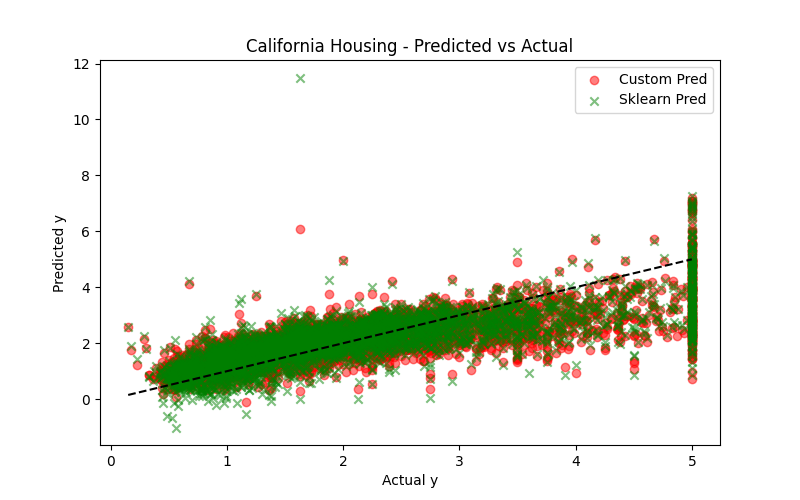
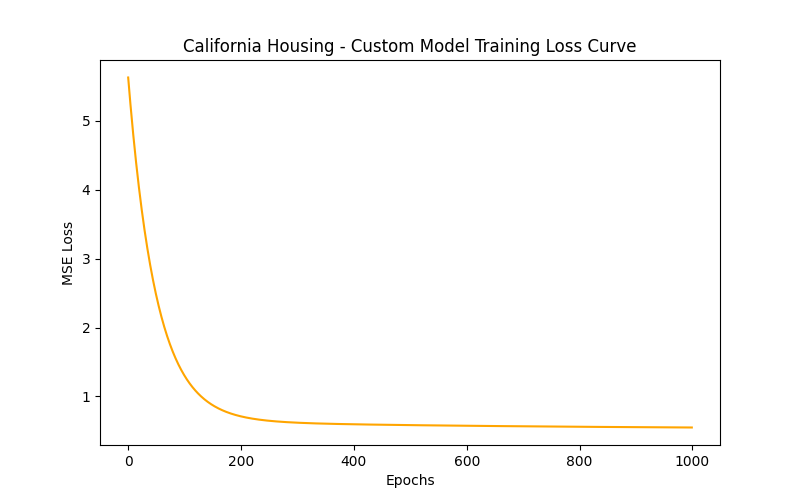
TASK 7: Create a Portfolio Webpage
Gained an understanding of the basics of creating a webpage using HTML and CSS. I developed a simple portfolio page that includes a short introduction about myself and applied basic styling with CSS. Below is the link to the code and a screenshot of the webpage:
TASK 9 : TINKERCAD:
Tinkercad is an online CAD tool for designing circuits, 3D models, and learning coding.
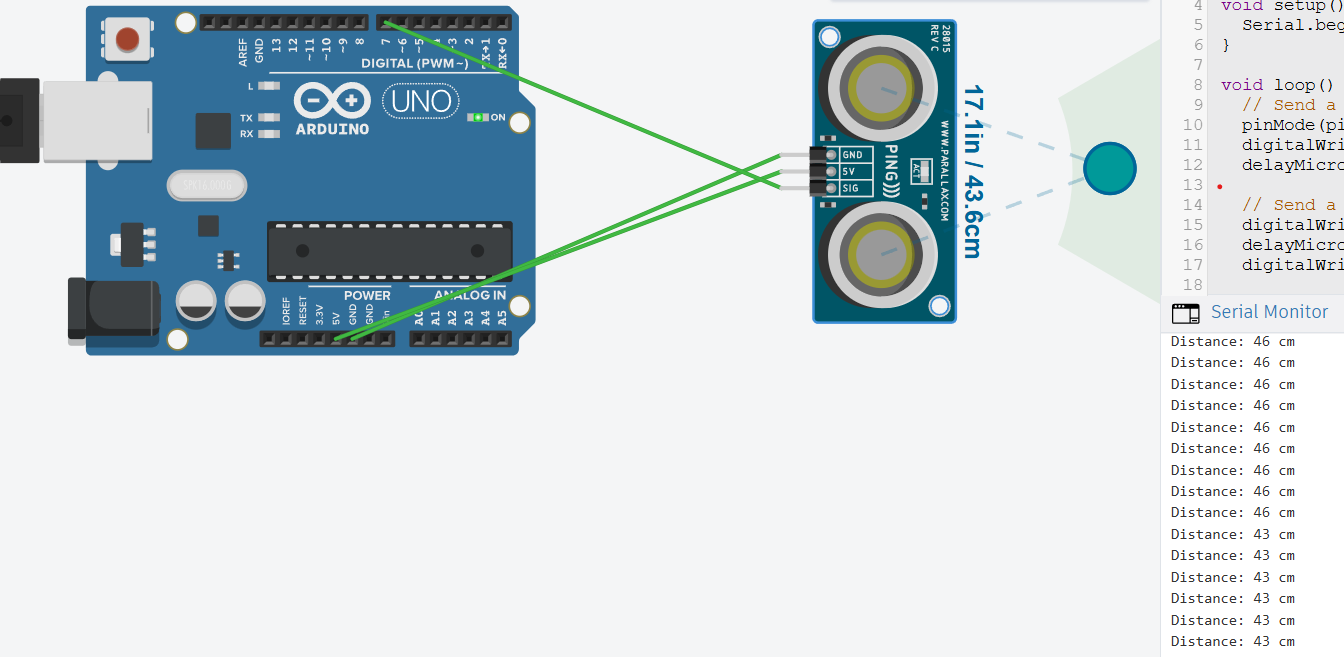
I created a Tinkercad account, explored example circuits, and simulated a circuit using an ultrasonic sensor to measure obstacle distance and display it on the serial monitor.
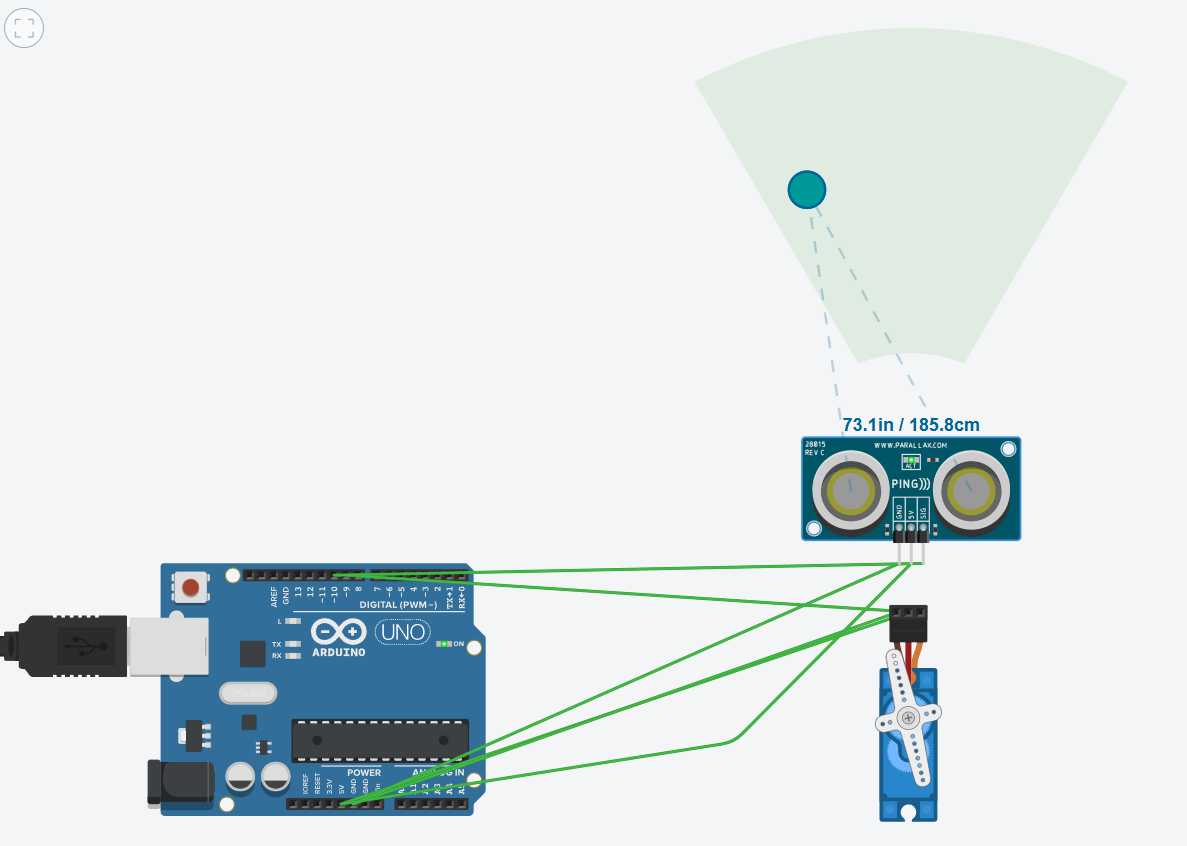
I also built a simple radar system with an ultrasonic sensor and servo motor, where the sensor measures distance and the servo rotates to cover a wider area for object detection.
TASK 10: Controlling DC Motors using Arduino and L298N
I explored controlling a 5V DC motor using an Arduino UNO and L298N H-Bridge motor driver. Using digital pins for direction and PWM for speed, I controlled the motor to rotate forward, backward, and stop.
The circuit was first simulated on Tinkercad, then implemented on hardware, and the results were recorded. The H-Bridge safely handles motor current, and PWM allows smooth speed variation, demonstrating basic DC motor control techniques.
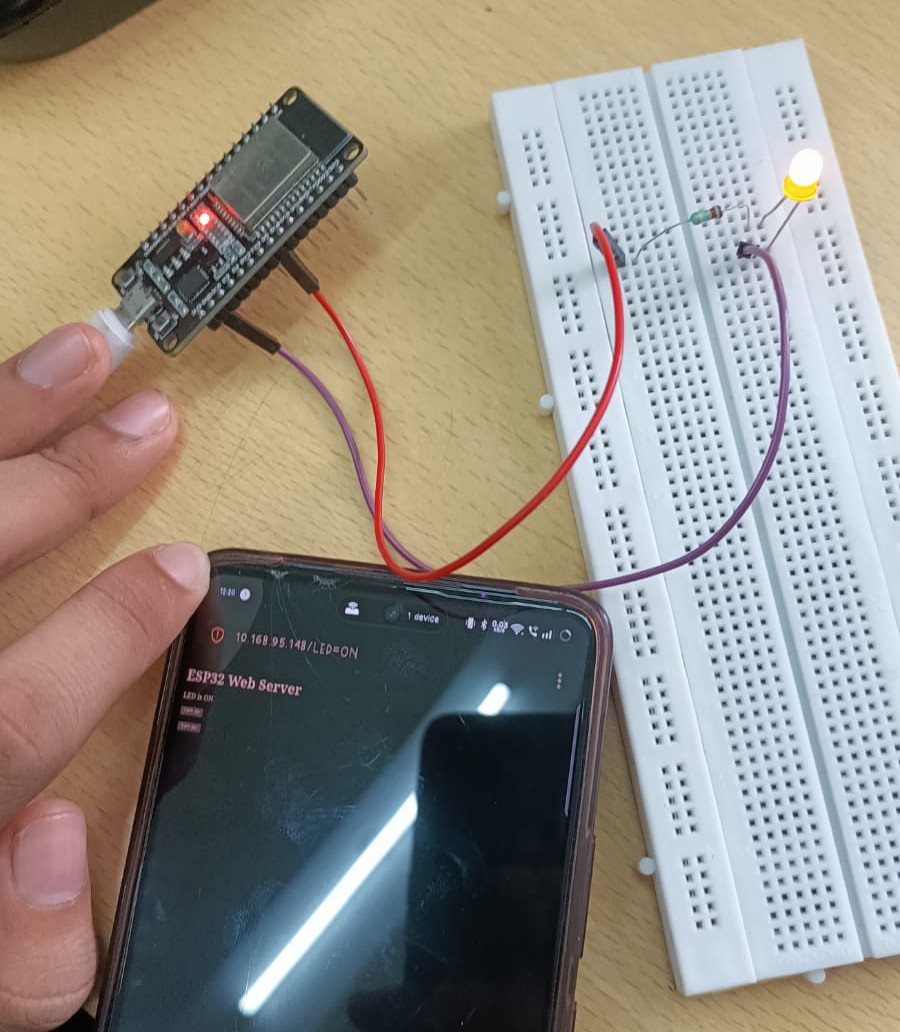
TASK 11: LED Toggle Using ESP32
ESP32 is a microcontroller with built-in wireless connectivity. Having learned the basics of ESP32 in a workshop, I set it up with the Arduino IDE and created a web server. By entering the IP address shown on the serial monitor into my friend’s phone, I was able to control the ESP32 remotely.

TASK 12: Soldering Prerequisites
Learned the basics of soldering, including how to use a soldering iron, solder, solder wick, and flux. A soldering iron is a hand tool that heats up when plugged into a standard AC outlet to melt solder around electrical connections. Solder is a metal alloy used to create a permanent bond between electrical components, while soldering flux cleans and prepares metal surfaces by removing oxides and impurities.
As part of this task, I soldered a LED onto a PCB, creating a dome-shaped blob of solder, and also learned the process of desoldering.
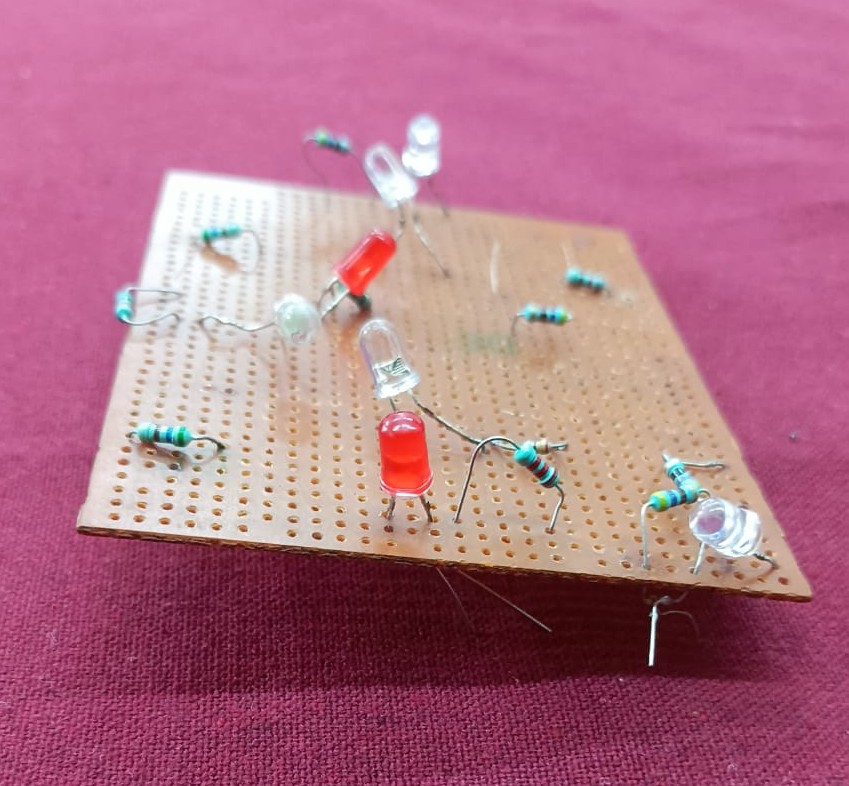
TASK 13: 555 Timer IC
The 555 Timer IC is an integrated circuit widely used for timing, delays, pulse generation, and oscillation. We have also used this IC in our lab sessions.
For this task, I configured the IC in Astable mode with a 60% duty cycle and built the circuit according to the provided diagram. The resulting square waveform was successfully observed on the oscilloscope, as shown below:
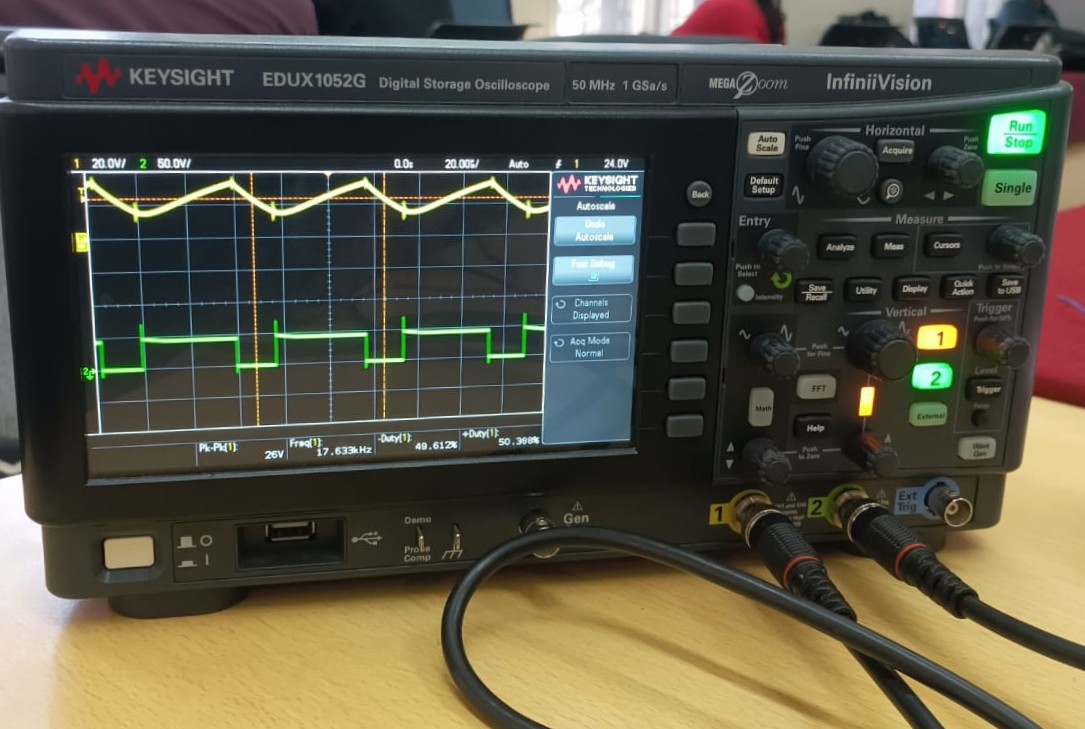
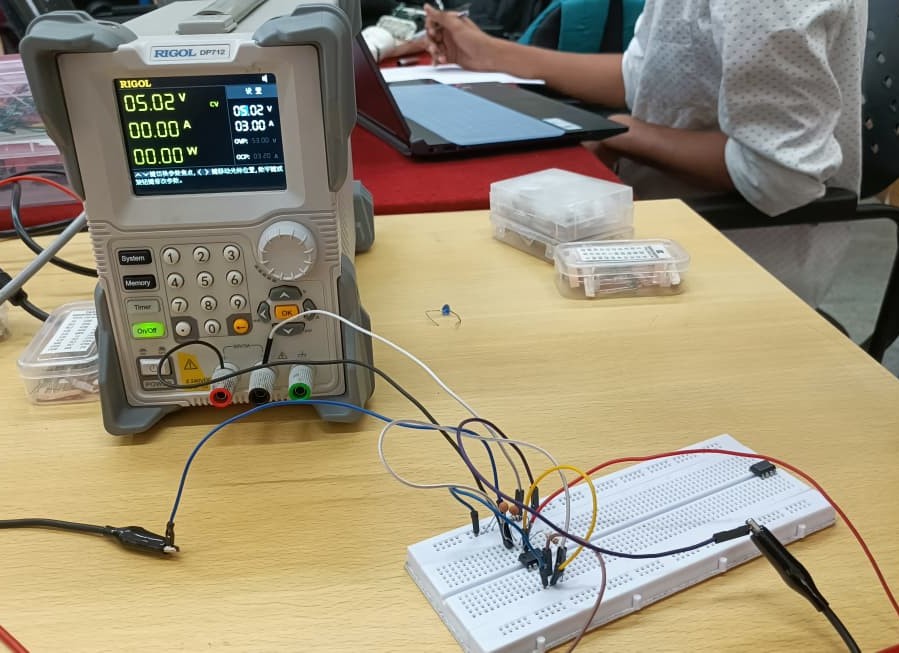
TASK 7: Karnaugh Maps and Deriving the Logic Circuit
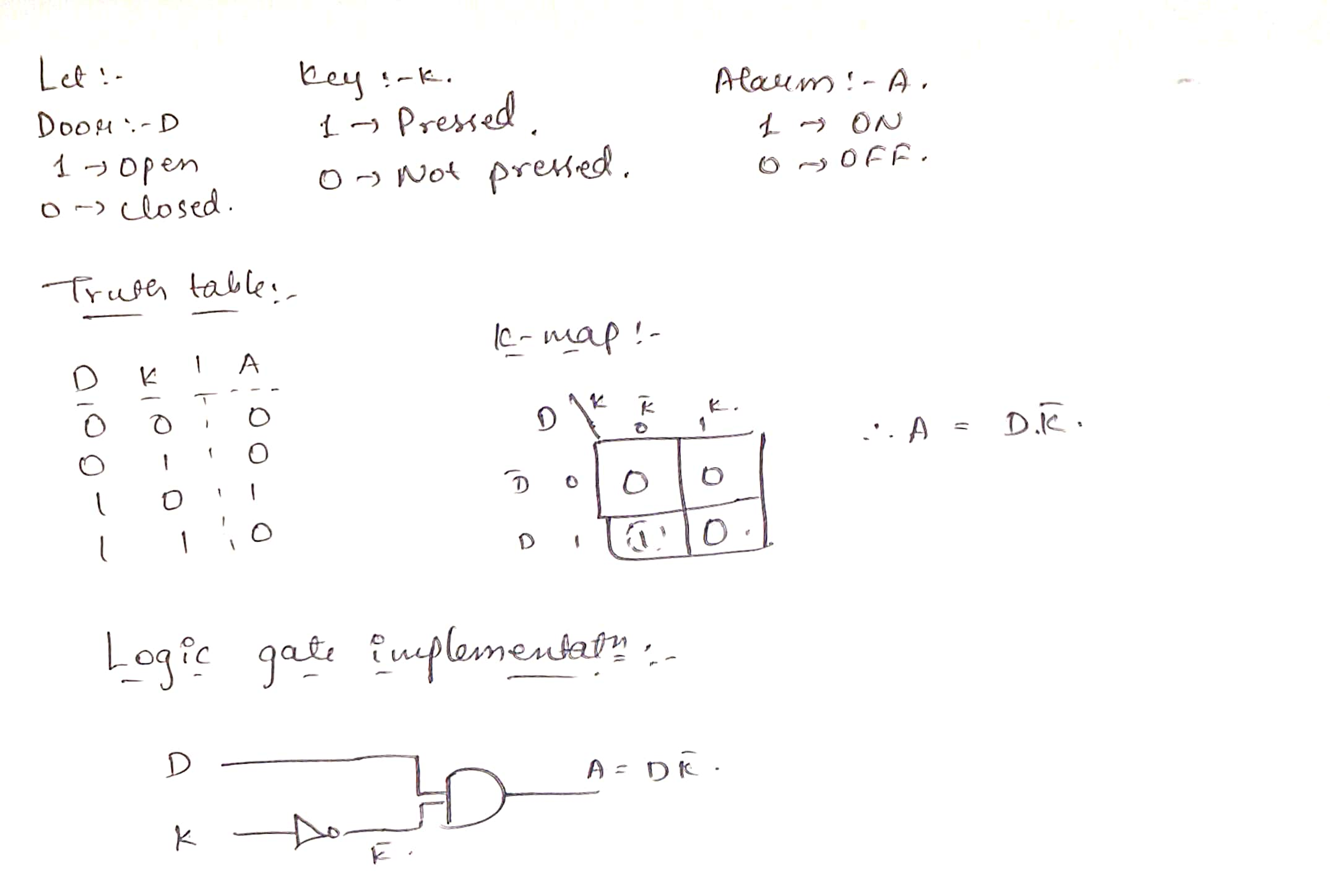
I designed a burglar alarm using simple logic circuits, based on the states of a door (open/closed) and a key (pressed/not pressed). Using Karnaugh maps, I identified the conditions required to trigger the alarm. The system was implemented with logic gates, where the alarm blinks only when the door is open and the key is not pressed. Push buttons were used to simulate the door and key inputs.
TASK 15: Active Participation
I attended a 3-day IoT and Embedded Systems workshop at BMSCE, conducted in collaboration with the IEEE Sensors Council. During the workshop, I learned the basics of Tinkercad, microcontrollers, and ESP32. I also built small projects such as a parking machine sensor, a distance tracker using an ultrasonic sensor, and a temperature and humidity sensor using ESP32 and Arduino. The workshop was conducted by tutors from Just Robotics, who provided excellent guidance.
TASK 15: L293D Motor Driver
Introduction
The L293D is a small IC that acts like a “bridge” between a microcontroller (like Arduino) and motors. It lets us control two DC motors or a stepper motor in both forward and backward directions.
How it Works
Inside the L293D, there are two H-bridges, each capable of controlling one motor. An H-bridge is a clever arrangement of switches (transistors) that lets current flow in either direction. This is what allows the motor to spin forward or backward.
PWM Speed Control
We can also control how fast the motor spins using Pulse Width Modulation (PWM). By rapidly turning the motor on and off at a certain ratio (duty cycle), we can make the motor run slower or faster.
Key Specs
- Can handle up to 600 mA per motor (1.2 A peak)
- Works with motor voltages from 4.5V to 36V
- 16-pin IC with built-in protection diodes
Applications
The L293D is widely used in small robotics projects:
- Driving wheels of a robot
- Controlling conveyor belts
- Stepper motor experiments with Arduino
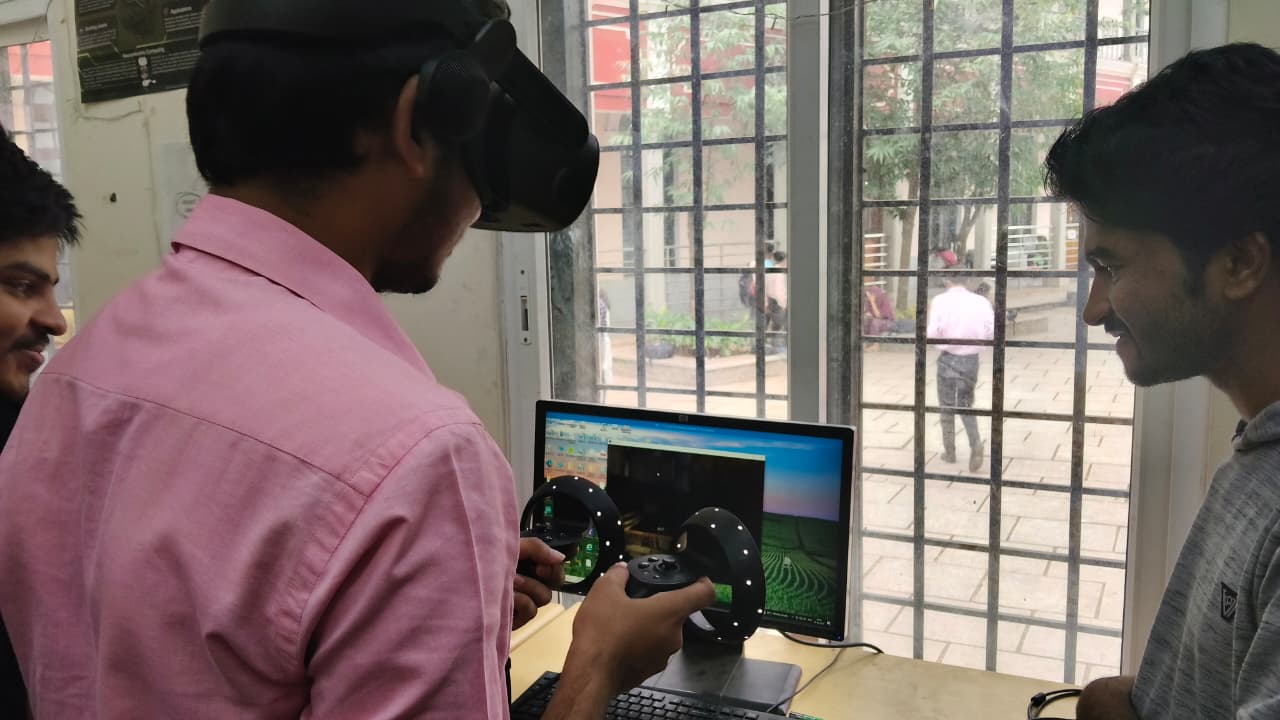
TASK 17: Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
Virtual Reality (VR) creates a fully immersive digital environment, replacing the real world, typically using VR headsets. Augmented Reality (AR) overlays digital content onto the real world, enhancing reality, and can be accessed via smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses.
VR fully immerses users in virtual spaces, while AR allows interaction with both real and digital elements. VR is mainly used in gaming, simulations, and virtual training, whereas AR is applied in navigation, retail, education, and healthcare.
Current trends include AI integration, improved hardware, enterprise adoption, healthcare applications, and the growth of the metaverse. The technology stack involves VR/AR headsets, motion sensors, game engines (Unity, Unreal), AR/VR SDKs (ARCore, ARKit), cloud computing, and AI/ML for enhanced interactivity.
Indian Companies:
- Simulanis – Industrial VR/AR training solutions
- Fusion VR – VR workshops and training
- Twin Reality – Virtual showrooms and metaverse applications
- Lucid Reality Labs – XR solutions for healthcare and education
- Variance Infotech – AR app development and 3D modeling
