Marvel Level 2 Report
2 / 1 / 2025
TASK 01: DOCKER
Docker is a containerization platform that allows developers to package, ship, and run applications in containers.
Docker Architecture
The Docker architecture consists of:
- Docker Engine: The Docker Engine is the runtime environment for containers. It provides a lightweight and portable way to run containers.
- Docker Hub: Docker Hub is a registry for Docker images. It provides a centralized location for users to share and manage their images.
- Docker Images: Docker images are templates for creating containers. They contain the application code, libraries, and dependencies required to run the application.
- Docker Containers: Docker containers are runtime instances of Docker images. They provide a isolated environment for running applications.
Key Benefits of Docker
Some of the key benefits of Docker include:
- Lightweight: Containers are much lighter than VMs, making them faster to spin up and down.
- Portable: Docker containers are highly portable and can run on any system that supports Docker, without requiring a specific environment or dependencies.
- Isolated: Containers provide a high level of isolation between applications, making it easier to manage and secure them.
- Efficient: Docker containers can help reduce infrastructure costs by allowing multiple applications to run on the same host, without the need for multiple VMs.


TASK 2: DOCKERFILE SPYWARE
A Dockerfile spyware would be a Dockerfile (a text file containing instructions for building a Docker image) that is designed to create a Docker image that contains spyware.
In other words, it's a recipe for building a Docker container that would secretly monitor and collect sensitive information from the host system or other containers, without the user's knowledge or consent.
 code
code
TASK 3: HASHING
Hashing is a process that takes input data (like a book title) and generates a unique fixed-length code, called a hash value or digest. This hash value represents the original data.
Here's how it works:
- You input data
- A hashing algorithm processes the data.
- The algorithm generates a unique hash value (a code).
- This hash value is stored or used for later reference.
Hashing is useful for:
- Data integrity: Hash values ensure data isn't tampered with or altered.
- Data storage: Hash values help quickly identify and retrieve data.
- Password security: Hash values are used to store passwords securely.
- Digital signatures: Hash values verify the authenticity of digital documents

TASK 4: NMap
Nmap (Network Mapper) is a free, open-source network scanning and exploration tool used to discover hosts, services, and operating systems on a computer network.
Nmap sends specially crafted packets to target hosts and analyzes the responses to gather information about:
- Host discovery: Identifying active hosts on a network.
- Port scanning: Detecting open ports and services running on a host.
- OS detection: Identifying the operating system and its version.
- Service version detection: Identifying the version of services running on a host.
Nmap is commonly used for:
- Network inventory and asset management
- Vulnerability scanning and assessment
- Penetration testing and security auditing
- Troubleshooting network connectivity issues

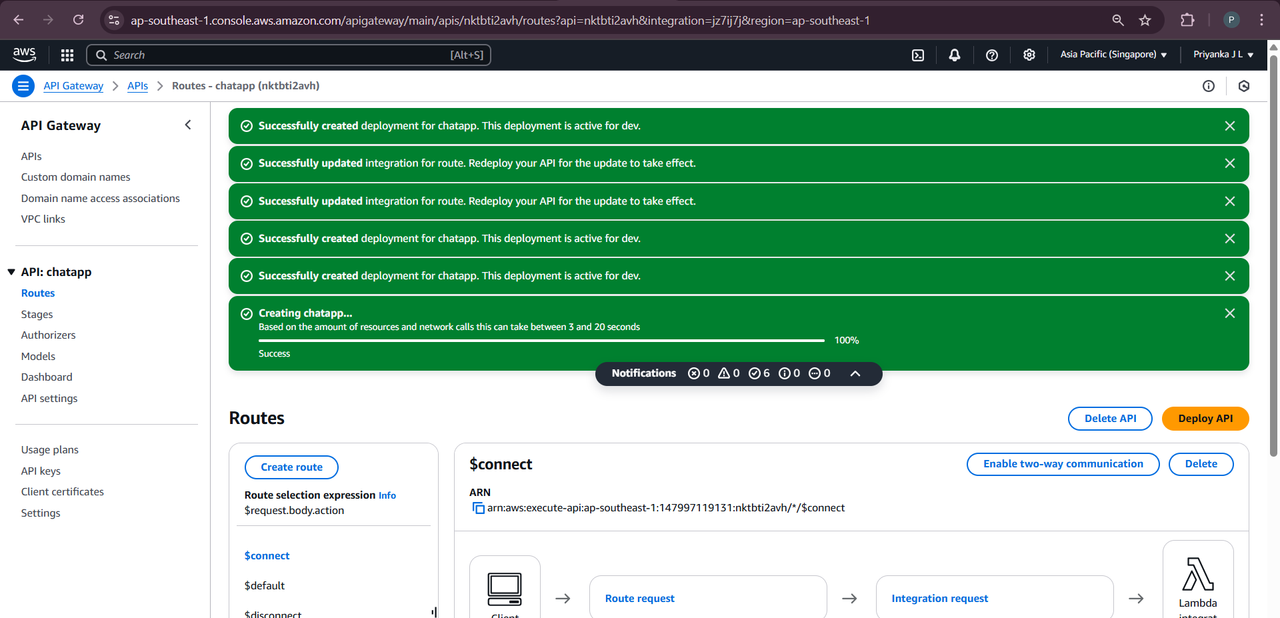
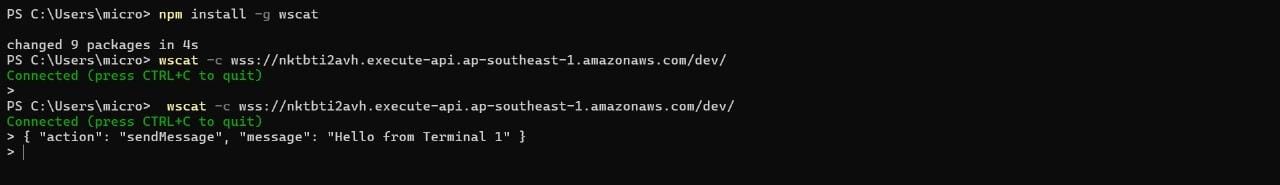
TASK 05: AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda is an event-driven, serverless Function as a Service (FaaS) provided by Amazon as a part of Amazon Web Services. It is designed to enable developers to run code without provisioning or managing servers. It executes code in response to events and automatically manages the computing resources required by that code.
This task enabled me to learn basics of running code on AWS Lambda without provisioning or managing servers.
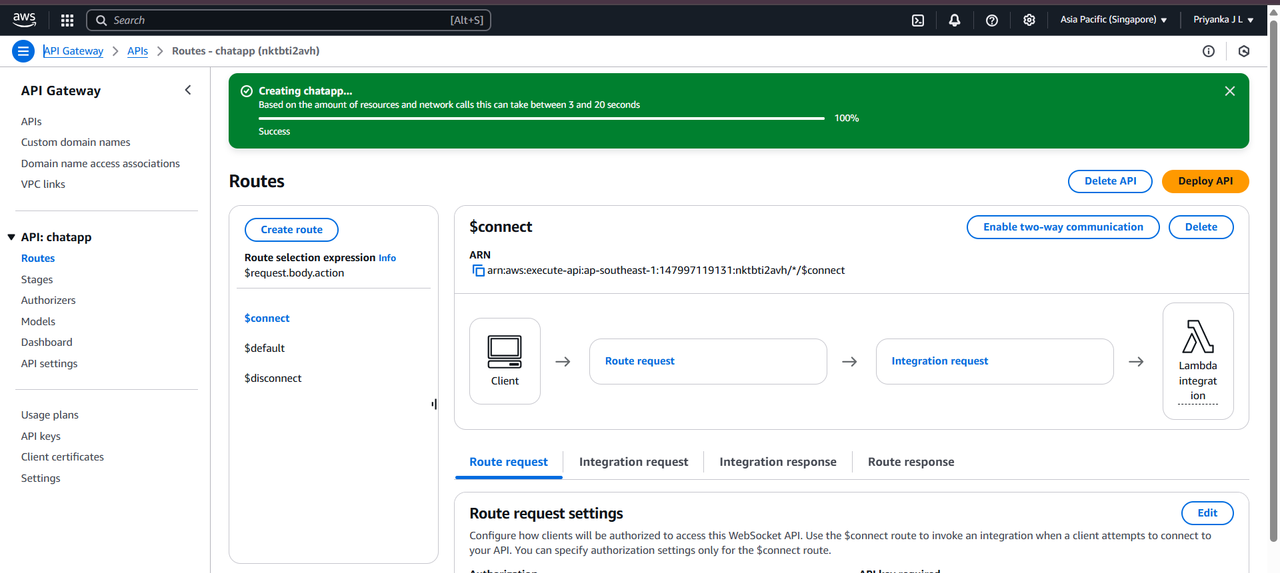
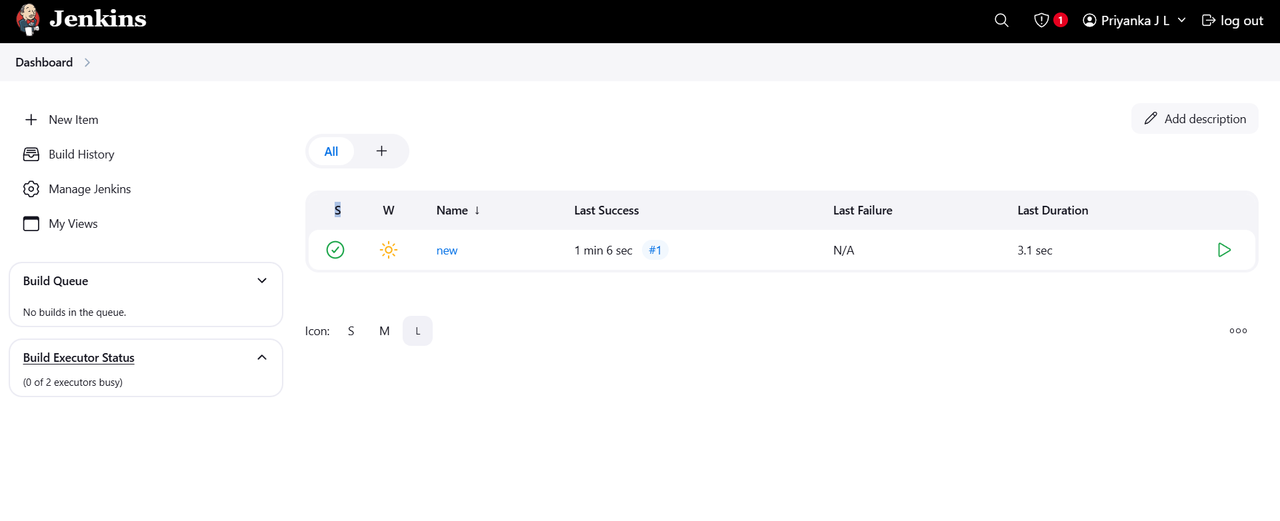
TASK 06: CI/CD (Continuous Integration & Continuous Delivery) - Intro to Jenkin
CI/CD is a practice in software development where code changes are automatically built, tested, and deployed. Continuous Integration (CI) focuses on integrating code changes frequently, while Continuous Delivery (CD) ensures that the code is deployable at any time. Jenkins, an open-source automation server, is widely used to implement CI/CD due to its flexibility and extensive plugin ecosystem.
Implementing a CI/CD pipeline using Jenkins significantly improves software development efficiency. Automating code integration, testing, and deployment reduces the risk of human error and accelerates the release cycle. Through this task, I gained hands-on experience with Jenkins and a deeper understanding of CI/CD practices.
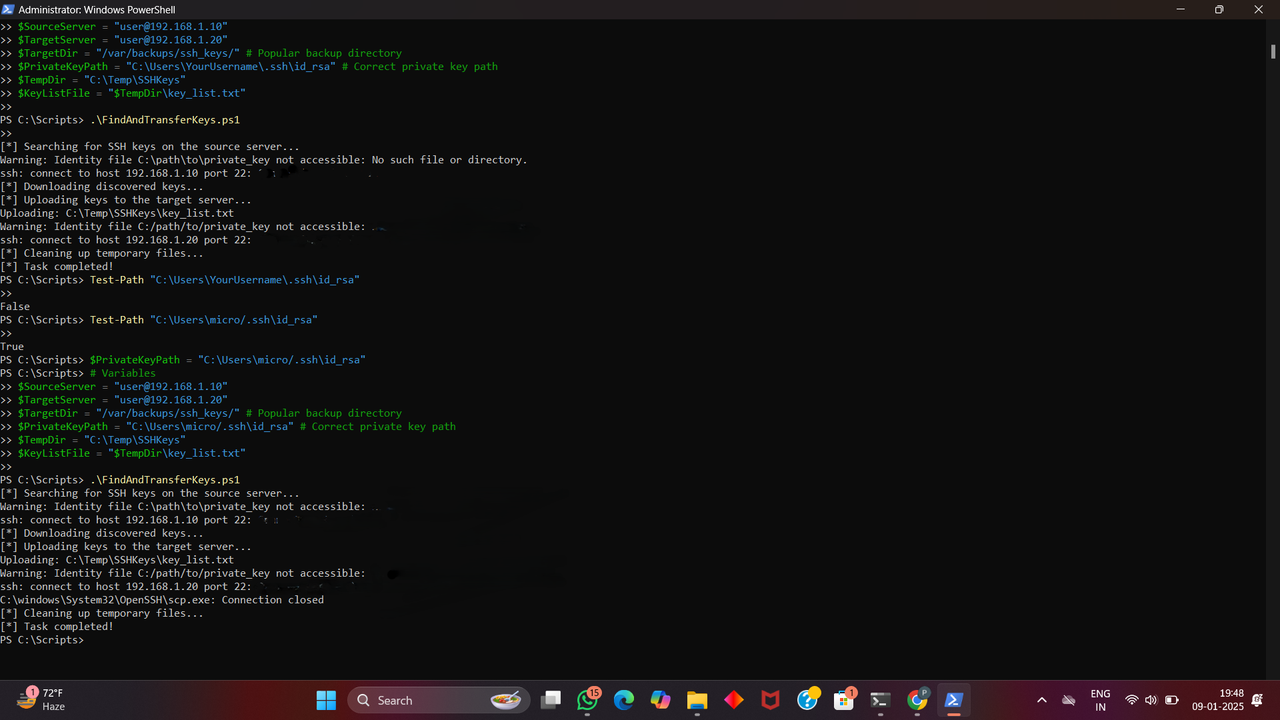
TASK 07: SSH
SSH (Secure Shell) is a protocol used for secure remote access between computers. Key-based authentication is a common method that uses a pair of cryptographic keys (private and public) to authenticate a user. Managing SSH keys efficiently and securely is crucial, especially when dealing with multiple servers.
Working on this task gave me practical experience with SSH automation. I learned how to script SSH logins, search for specific file types (like SSH keys), and securely transfer them using SCP. Additionally, I understood the importance of handling SSH keys securely to prevent unauthorized access.
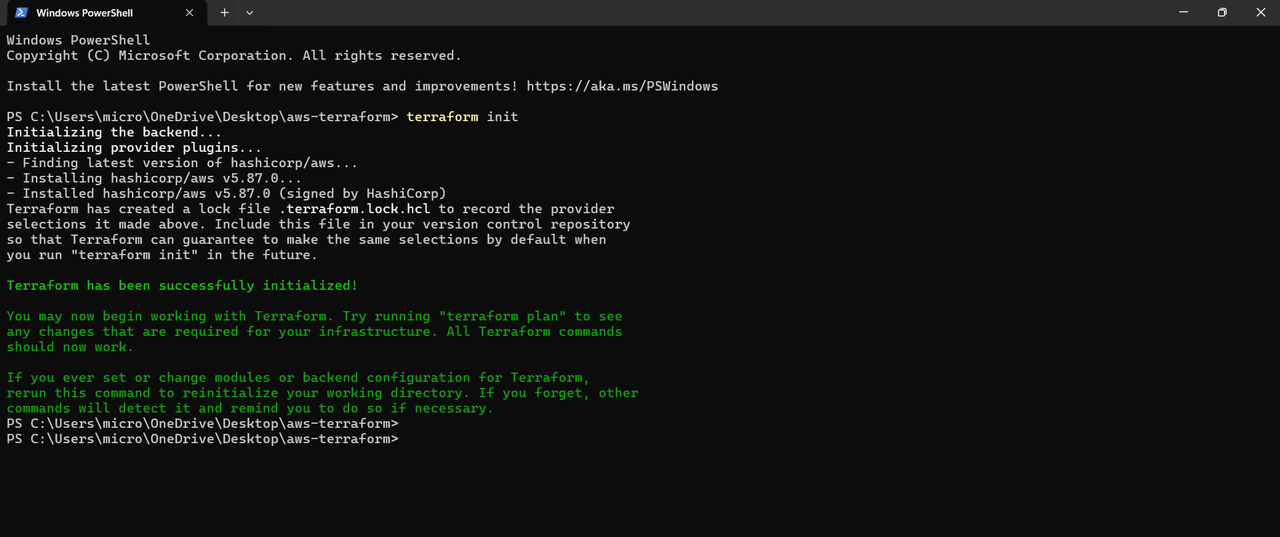
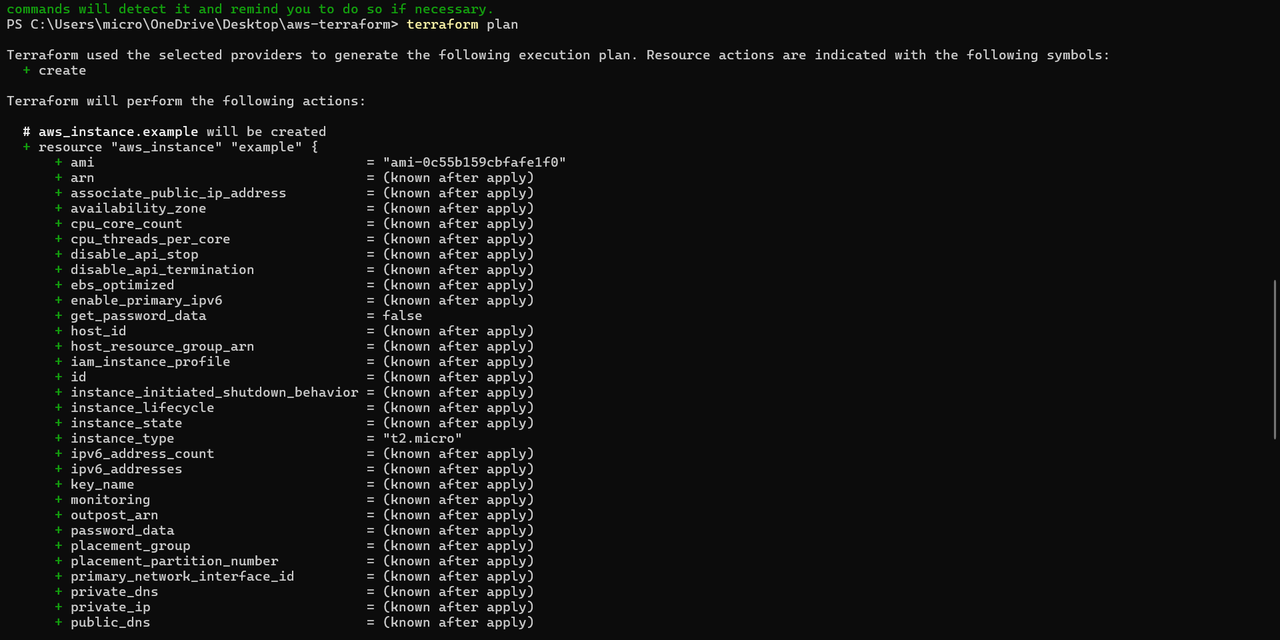
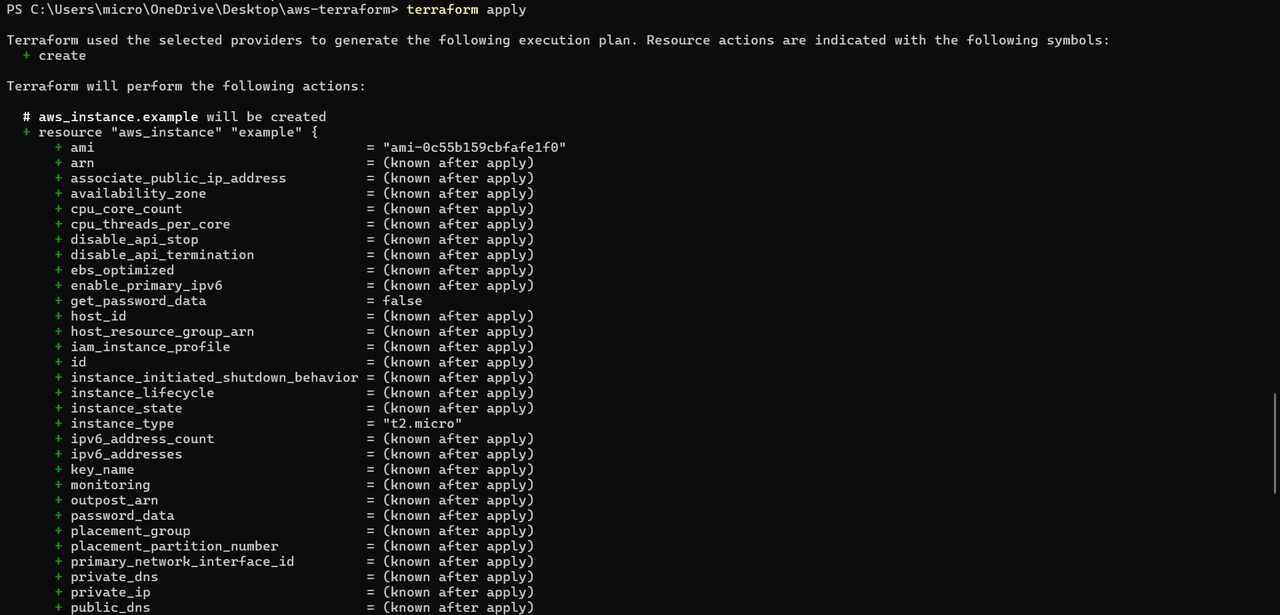
TASK 08: Terraform
Terraform, an open-source Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tool developed by HashiCorp, enables developers to define and provision data center infrastructure using a declarative configuration language , meaning it is a tool that helps you set up and manage your cloud resources (like servers, databases, and networks) using simple code instead of manually clicking through a cloud provider’s website.
TASK 09: Web Scraping and Automation - Flight Ticket Price Analysis
Web scraping involves using a program to extract data from websites automatically. In this context, the goal was to collect flight prices to identify cheaper booking opportunities.
Selenium is a popular Python library that allows automation of web browsers. It is often used for tasks like form filling and interacting with dynamic content.
This task provided hands-on experience with web scraping using Selenium, especially in automating browser interactions. I learned how to navigate dynamic web pages, handle form filling, and efficiently extract flight prices. Additionally, I gained insight into sending automated emails using Python’s smtplib, which was a useful addition to the project.
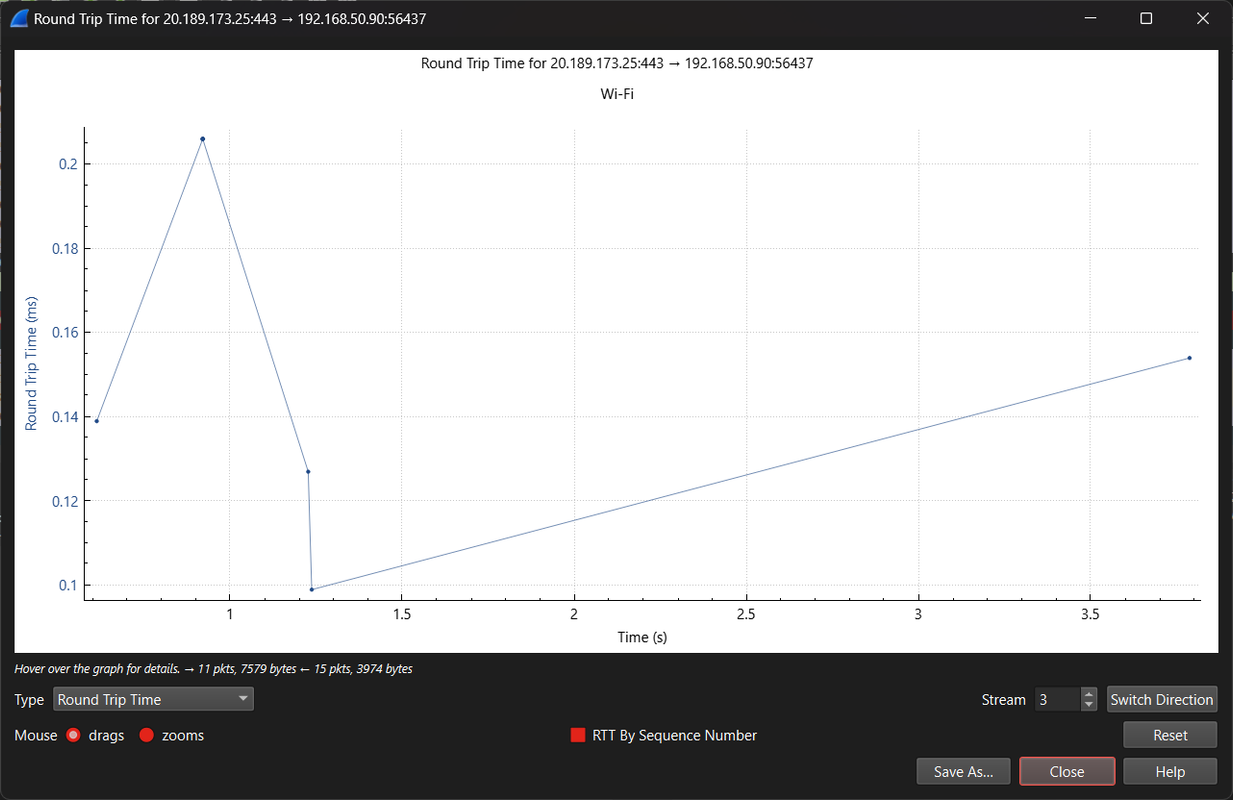
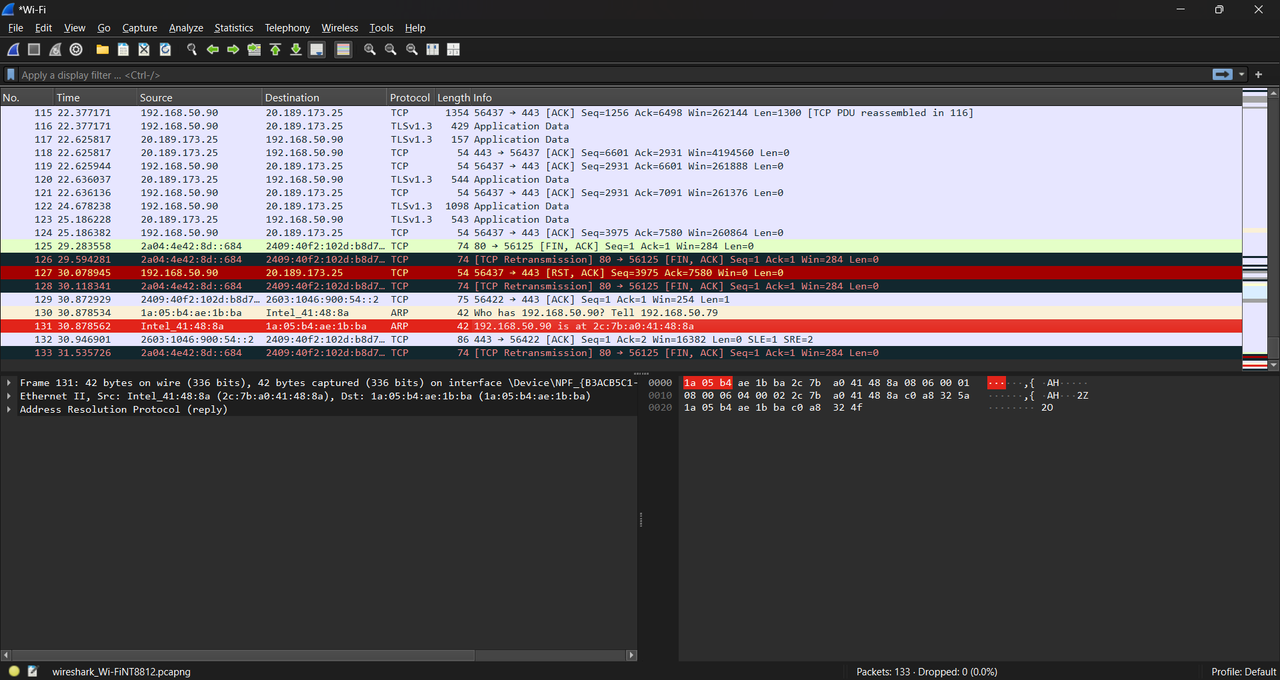
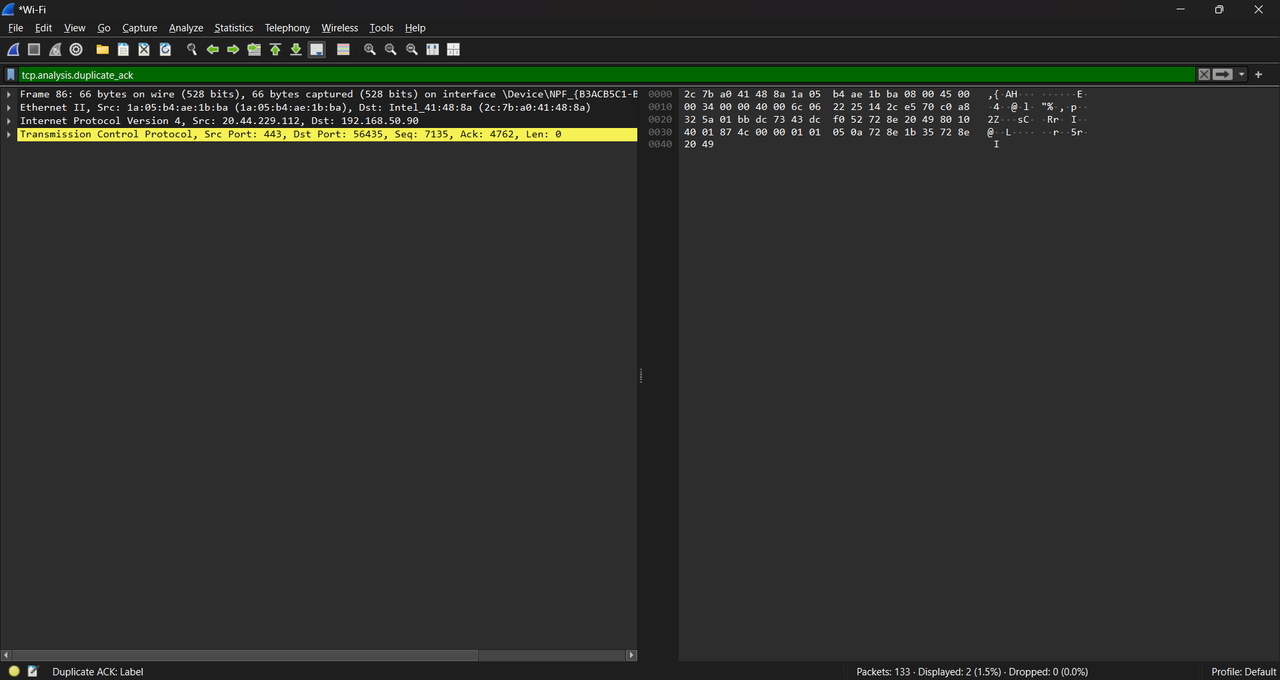
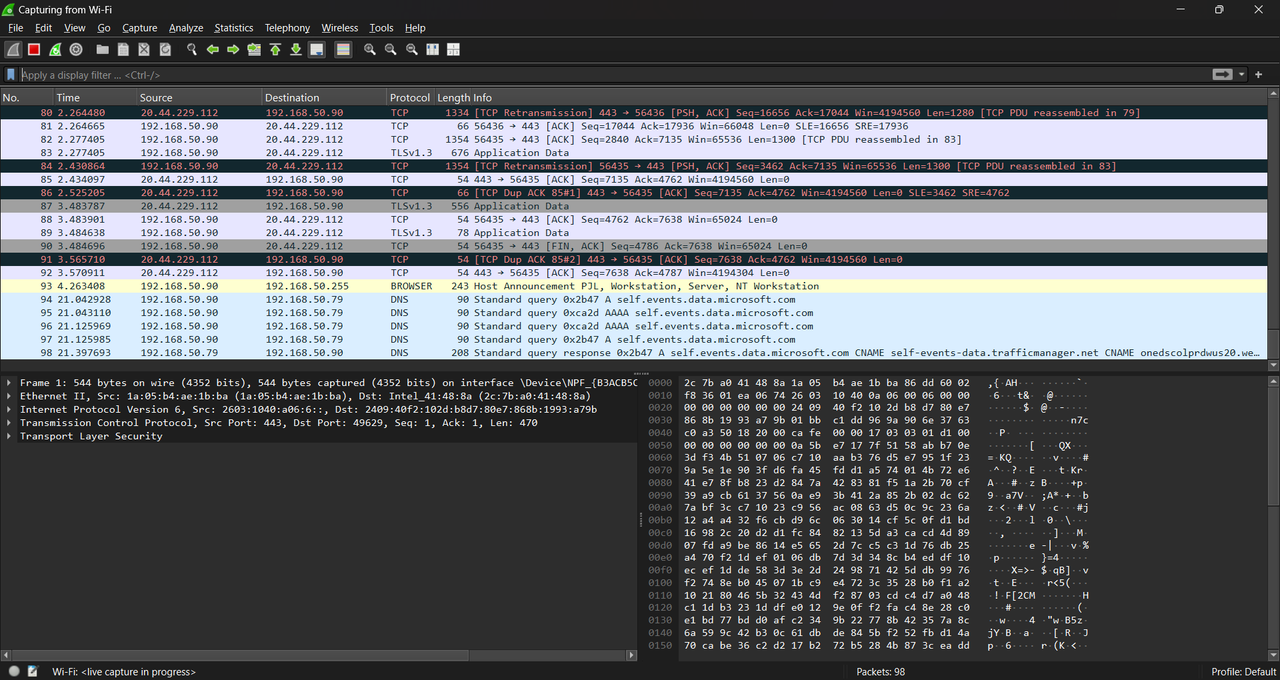
TASK 10: Wireshark
Wireshark is a free and open-source packet analyzer. It is used for network troubleshooting, analysis, software and communications protocol development, and education. Learn about network trafficking, fundamentals of Wireshark Analysis, and identify potential security threats.
I explored the use of Wireshark, a powerful and free network packet analyzer. Wireshark is widely used for diagnosing network issues, analyzing traffic patterns, and identifying potential security threats. The goal of the task was to learn how to detect network problems like latency, packet loss, or retransmissions and analyze traffic data effectively.