

Exploring UAVs and Drones: Configurations, Environmental Factors, and Operations
Introduction
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, have revolutionized multiple industries, including agriculture, defense, logistics, and entertainment. This report explores key aspects of UAVs and drones: their configurations, environmental conditions affecting flight, their movements and maneuvers, and the use of transmitters for operation.
1. Understanding Different UAV/Drone Configurations
UAVs and drones come in various configurations, each designed for specific purposes. Below are the primary configurations:
Fixed-Wing Drones:
- Design: Resemble airplanes with fixed wings.
- Characteristics: Capable of long flights with high efficiency.
- Applications: Aerial mapping, surveillance, and agricultural monitoring.
Rotary-Wing Drones:
- Design: Equipped with multiple rotors (e.g., quadcopters, hexacopters).
- Characteristics: Highly maneuverable and capable of vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL).
- Applications: Photography, delivery, and inspection.
Hybrid Drones:
- Design: Combine fixed-wing and rotary-wing features.
- Characteristics: Offer the endurance of fixed-wing drones and the versatility of rotary-wing drones.
- Applications: Advanced reconnaissance and long-range delivery.
Single-Rotor Helicopter Drones:
- Design: Feature one large rotor and a smaller tail rotor.
- Characteristics: High payload capacity and efficient hover capabilities.
- Applications: Lifting heavy objects and crop dusting.
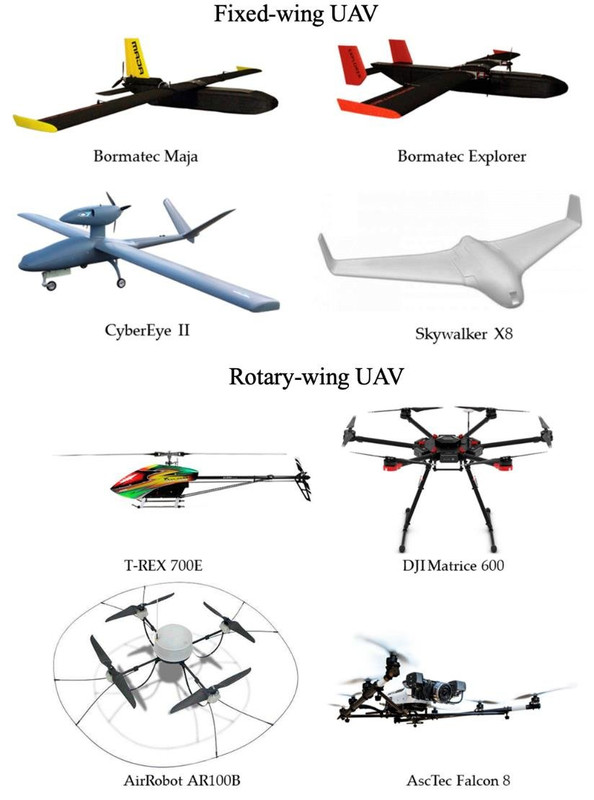

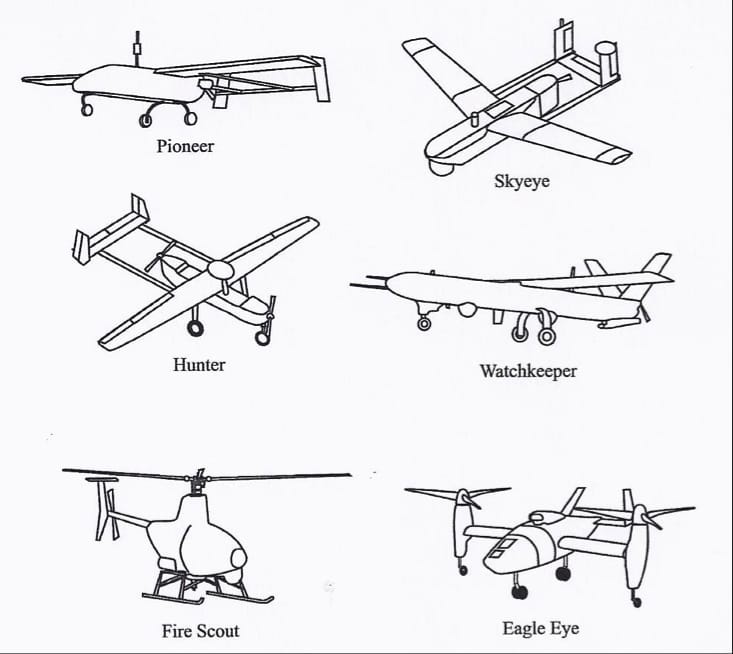
2. Environmental Conditions Affecting Flight
Several environmental factors can influence UAV and drone performance:
Wind:
- Strong winds can destabilize the drone, especially smaller models.
- Wind speed above the drone’s threshold may lead to a loss of control or damage.
Temperature:
- Extreme temperatures (hot or cold) affect battery performance and motor efficiency.
- High heat can cause overheating, while cold reduces battery capacity.
Rain and Humidity:
- Moisture can damage electronic components and reduce visibility for optical sensors.
Altitude:
- Higher altitudes result in thinner air, which reduces lift efficiency for fixed-wing drones and rotor performance for rotary-wing drones.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI):
- Urban areas with high EMI from power lines and radio towers can disrupt the drone’s GPS and communication systems.
3. Observing UAV/Drone Movements and Maneuvers
Drones execute various movements and maneuvers depending on their configuration and use case:
Basic Movements:
- Ascend/Descend: Vertical movement controlled by the throttle.
- Pitch: Forward and backward tilting for forward or reverse movement.
- Roll: Side-to-side tilting for lateral movement.
- Yaw: Rotational movement for changing the drone’s direction.
Advanced Maneuvers:
- Hovering: Maintaining a stable position mid-air (rotary-wing drones).
- Orbiting: Flying in a circular path around a point of interest.
- Waypoint Navigation: Following a pre-programmed path using GPS.
- Acrobatics: Performing flips and rolls (mainly for racing drones).
4. Learning How to Use a Transmitter
A transmitter is the primary tool for controlling a UAV or drone. Here’s how it works:
Basic Components:
- Throttle Stick: Controls altitude and speed.
- Yaw Stick: Adjusts the drone’s rotation.
- Pitch Stick: Moves the drone forward or backward.
- Roll Stick: Moves the drone left or right.
- Switches and Knobs: Customize flight modes and control auxiliary functions.
Pre-Flight Checklist:
- Check battery levels of both the drone and transmitter.
- Ensure proper calibration of the gyroscope and compass.
- Perform a range test to verify communication strength.
Flight Modes:
- Manual Mode: Provides complete control to the pilot, ideal for experienced operators.
- GPS Mode: Uses satellite navigation for stable and precise control.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): Automatically guides the drone back to the takeoff point.
My experience with simulation flying
 this image showcases different types of drones.
this image showcases different types of drones.
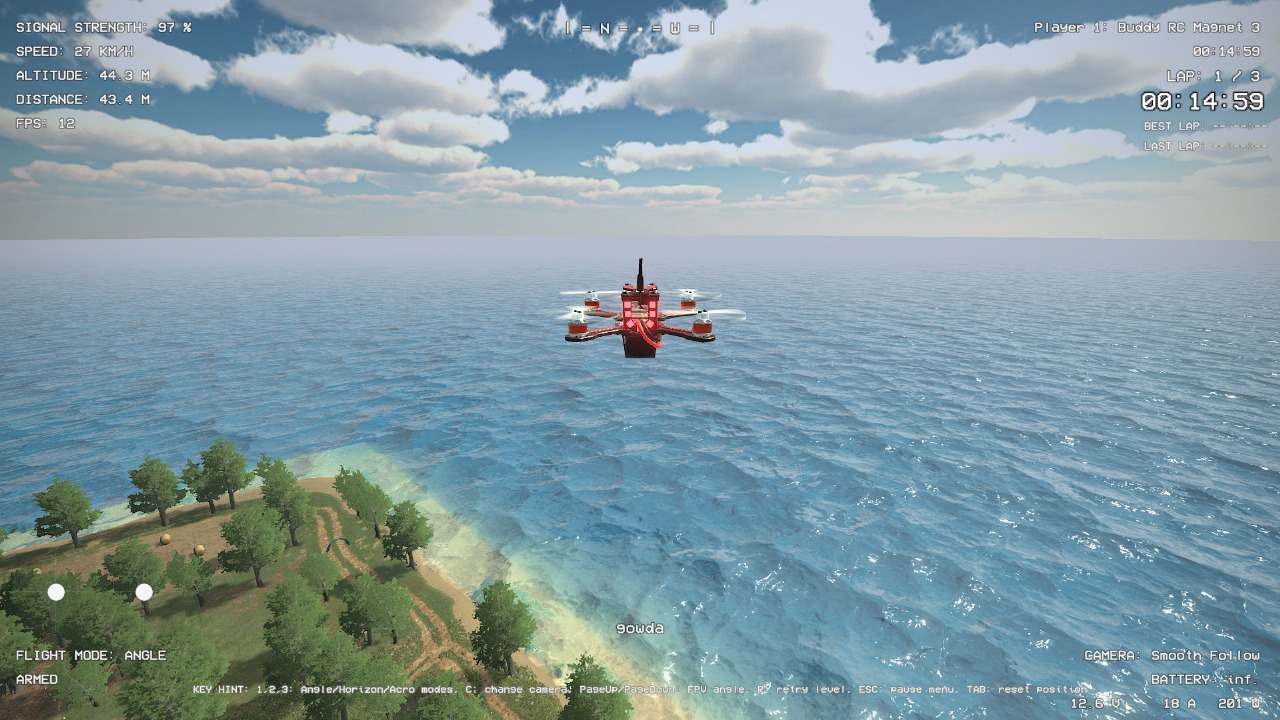 this image showcases the flight of drone over one particular environment. I also flew the drone on different available environments.
this image showcases the flight of drone over one particular environment. I also flew the drone on different available environments.