
RESOURCE · 2/1/2025
Edge Computing: Decentralizing Data Processing
Revolutionizing Data Processing by Bringing Power Closer to the Source

Introduction
Edge computing is a transformative technology that is reshaping how we process data in real-time. By bringing computation closer to the data source (at the "edge" of the network), edge computing reduces latency, optimizes bandwidth, and ensures faster, more efficient decision-making. This is especially critical in fields like the Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation.
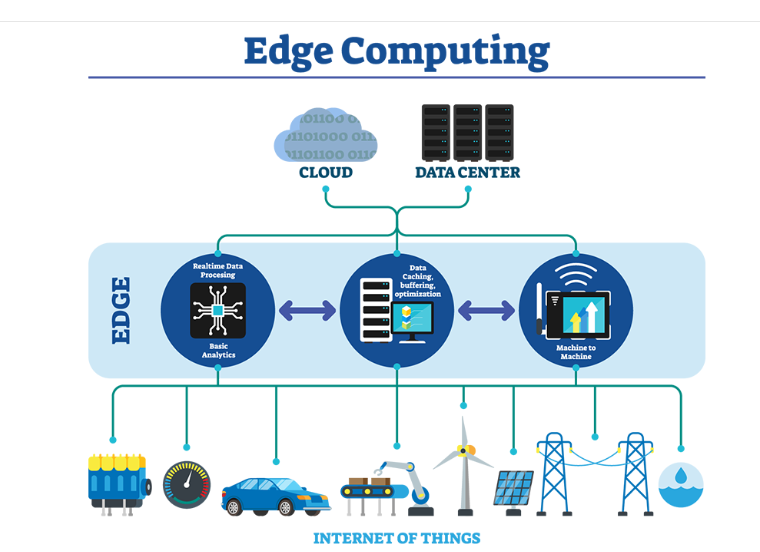
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing involves processing data at or near the location where it is generated, rather than relying on distant cloud servers. This shift from centralized to decentralized processing allows for immediate data analysis, providing real-time insights and faster responses to critical events. It is essential for applications that require low latency and immediate action.
Why is Edge Computing Important?
Traditional cloud computing involves sending data to a central server for processing, which can lead to delays (latency) and bandwidth issues. Edge computing addresses these challenges by reducing the distance data must travel, enabling:
- Real-time decision-making
- Improved efficiency and speed
- Reduced reliance on centralized servers
This makes edge computing crucial for modern technologies like autonomous vehicles, industrial IoT, and smart cities.
Applications of Edge Computing
-
IoT (Internet of Things) : Edge computing is the backbone of many IoT devices. By processing data locally, devices like smart home systems, sensors, and wearables can respond instantly to changes in their environment.
-
Autonomous Vehicles : Self-driving cars rely on edge computing to process data from cameras, sensors, and GPS systems in real time. This ensures immediate responses to critical events, like avoiding obstacles or adjusting speed.
-
Smart Cities: In smart cities, thousands of connected devices and sensors monitor traffic, weather, pollution, and public safety. Edge computing helps process this data locally, making it possible to react quickly and efficiently.
-
Healthcare: Wearable health devices and remote monitoring systems rely on edge computing to analyze patient data in real-time. This enables quicker medical responses and helps prevent emergencies.
-
Industrial Automation Factories use edge computing to monitor production lines and machinery. By processing data locally, it helps predict equipment failure and optimize manufacturing operations.
Why Edge Computing is Exciting
Edge computing enables real-time data processing, which is crucial for applications that require immediate action. It is particularly exciting because it reduces dependency on centralized cloud servers and opens the door to new opportunities in autonomous systems, IoT, healthcare, and smart infrastructure.
The ability to process data at the edge makes these systems more efficient, scalable, and responsive, which is why edge computing is becoming a critical part of the next generation of technology.
Conclusion
Edge computing is reshaping how we process and manage data in an increasingly connected world. By decentralizing data processing, it brings faster insights, reduces latency, and opens new possibilities for industries like autonomous vehicles, healthcare, and IoT. As technologies like 5G roll out and the need for real-time processing grows, edge computing will continue to play a pivotal role in driving innovation.