
RESOURCE · 21/12/2023
Semiconductors: Enabling the Digital Revolution
A short technical article by maxus_red

This Article is yet to be approved by a Coordinator.

RESOURCE · 21/12/2023
A short technical article by maxus_red

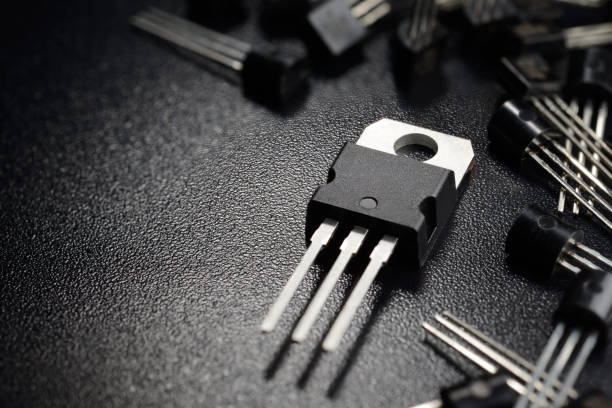 \nSemiconductor transistors, functioning as either switches or amplifiers, are the building blocks of electronic circuits. Their invention marked a paradigm shift, enabling the development of smaller and more efficient electronic devices.\n\n### Integrated Circuits\n
\nSemiconductor transistors, functioning as either switches or amplifiers, are the building blocks of electronic circuits. Their invention marked a paradigm shift, enabling the development of smaller and more efficient electronic devices.\n\n### Integrated Circuits\n \nThe advent of Integrated Circuits (ICs) marked a revolutionary leap in semiconductor technology. These intricate assemblies of transistors and other components on a single chip have facilitated the creation of powerful, compact electronic devices such as computers and smartphones.\n\n### Sensors\n
\nThe advent of Integrated Circuits (ICs) marked a revolutionary leap in semiconductor technology. These intricate assemblies of transistors and other components on a single chip have facilitated the creation of powerful, compact electronic devices such as computers and smartphones.\n\n### Sensors\n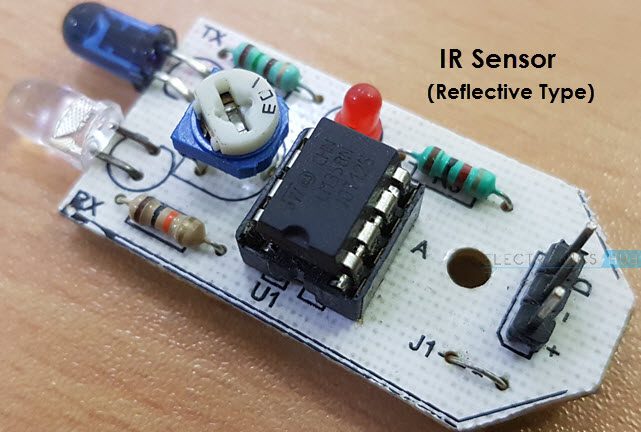 \nSemiconductors are instrumental in the sensor technology landscape. They play a pivotal role in converting physical signals into electrical signals, a crucial function in applications ranging from environmental monitoring to healthcare and industrial automation.\n\n## Interesting Facts\n\nUnveiling the mysteries of semiconductors reveals fascinating insights into their dominance in the technological domain:\n\n1. Silicon Dominance: Silicon stands as the undisputed king among semiconductor materials. Its abundance, combined with favorable electrical properties, has made it the cornerstone of the semiconductor industry.\n\n2. Moore's Law: Coined by Gordon Moore, this empirical observation asserts that the number of transistors on a microchip approximately doubles every two years. This law has held true for decades, driving the relentless progress of technology.\n
\nSemiconductors are instrumental in the sensor technology landscape. They play a pivotal role in converting physical signals into electrical signals, a crucial function in applications ranging from environmental monitoring to healthcare and industrial automation.\n\n## Interesting Facts\n\nUnveiling the mysteries of semiconductors reveals fascinating insights into their dominance in the technological domain:\n\n1. Silicon Dominance: Silicon stands as the undisputed king among semiconductor materials. Its abundance, combined with favorable electrical properties, has made it the cornerstone of the semiconductor industry.\n\n2. Moore's Law: Coined by Gordon Moore, this empirical observation asserts that the number of transistors on a microchip approximately doubles every two years. This law has held true for decades, driving the relentless progress of technology.\n \n\n3. Quantum Mechanics: The behavior of electrons in semiconductors is intricately linked to quantum mechanics. Manipulating quantum effects has led to the development of quantum computers and advanced semiconductor devices, pushing the boundaries of computational capabilities.\n\n4. Photonic Semiconductors: Beyond their electronic applications, semiconductors also play a pivotal role in photonics. Photonic semiconductors facilitate the transmission of information using photons, enabling high-speed communication and advancements in optical technologies.\n\n## Conclusion\n\nIn conclusion, semiconductors stand as the silent architects of the digital revolution, driving progress in technology, communication, and beyond. Their versatile applications and constant innovation underscore their paramount importance in shaping the future of electronics and ushering in a new era of technological possibilities.\n
\n\n3. Quantum Mechanics: The behavior of electrons in semiconductors is intricately linked to quantum mechanics. Manipulating quantum effects has led to the development of quantum computers and advanced semiconductor devices, pushing the boundaries of computational capabilities.\n\n4. Photonic Semiconductors: Beyond their electronic applications, semiconductors also play a pivotal role in photonics. Photonic semiconductors facilitate the transmission of information using photons, enabling high-speed communication and advancements in optical technologies.\n\n## Conclusion\n\nIn conclusion, semiconductors stand as the silent architects of the digital revolution, driving progress in technology, communication, and beyond. Their versatile applications and constant innovation underscore their paramount importance in shaping the future of electronics and ushering in a new era of technological possibilities.\n