BLOG · 11/6/2025
Level 2 MECHANICAL TASKS

This Article is yet to be approved by a Coordinator.
Mechanical Design
Mechanical Design Basics
- Involves creating and improving designs for machines, equipment, or processes.
Difference Between Drawing, Drafting, and Design
- Drawing: A rough sketch to convey ideas.
- Drafting: Precise, scaled engineering drawing using standards.
- Design: A complete plan or prototype, including analysis.
CAD, CAM, CAE
- CAD: Computer-aided design (2D/3D models and drawings).
- CAM: Computer-aided manufacturing (machine control, NC programming).
- CAE: Computer-aided engineering (simulation).
Types of Projections
- Orthographic: Parallel lines.
- Oblique: Drawn at 45° angle.
- Perspective: Realistic 3D look.
Orthographic Projections
- 1st Angle and 3rd Angle projections are used.
- 2nd and 4th Angle are not used due to overlapping views.
1. Introduction to Engineering Drawing
Isometric and Orthographic Projections


2D Drawings in CAD
- Objective: To generate 2D Drawings
- Platform: Fusion 360
2D Drafting
Objective: To draw Level 2 Sierpenski Triangle and generate a drawing sheet with dimensions neatly labelled.

3D Drafting
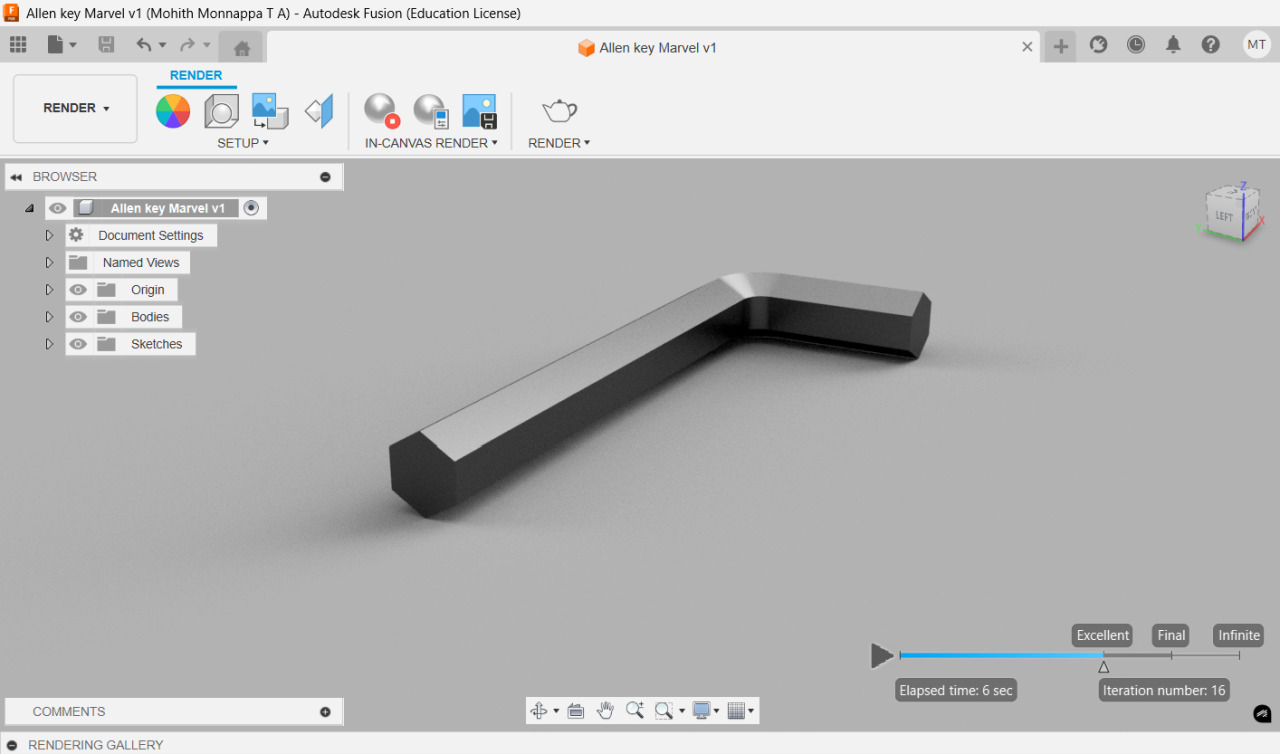
Task 1
- Objective: To draw an Allen key and generate a labelled drawing sheet for the same. Along with a 3d model for the same in Fusion 360.
- Parameters: Length - 55mm Width - 20mm Size - 3mm
- Platform: Fusion 360
2. 3D Modelling
Solid Modelling
Objective:
- To design a simple airfoil for an HTOL aircraft using Fusion360. Make use of Plug-Ins and add ons to generate a NACA airfoil.
- Understand the nomenclature of NACA profile and understand the meaning of those terms.
- Understand the basic aspects of a wing design like leading, trailing edge and camber line.
What is an Airfoil?
The cross-sectional shape of an aircraft's wing is called as an airfoil. It is responsible for generation of lift of aircraft.
Generation of Lift:
- Lift is created because of the pressure difference in the upper and lower surface of the airfoil.
- The flow of air is faster in the upper surface then the lower surface ( velocity is inversely proportional to pressure).
- So the air pressure is lesser in the upper surface and higher in the lower surface.
- The lift depends on Shape, Velocity, Density, Surface area, Angle of attack of the airfoil.
- Angle of attack is the angle between the wind and the chord line. As angle of attack increases, the lift increases.
- As the angle of attack increases after a threshold angle, lift decreases and drag increases. This is called as Stall. Angle at which Stall occurs is called Stall angle.
Some Basic Terms of an Airfoil: