

Gaganyaan Mission: India's Manned Spaceflight Program
Introduction
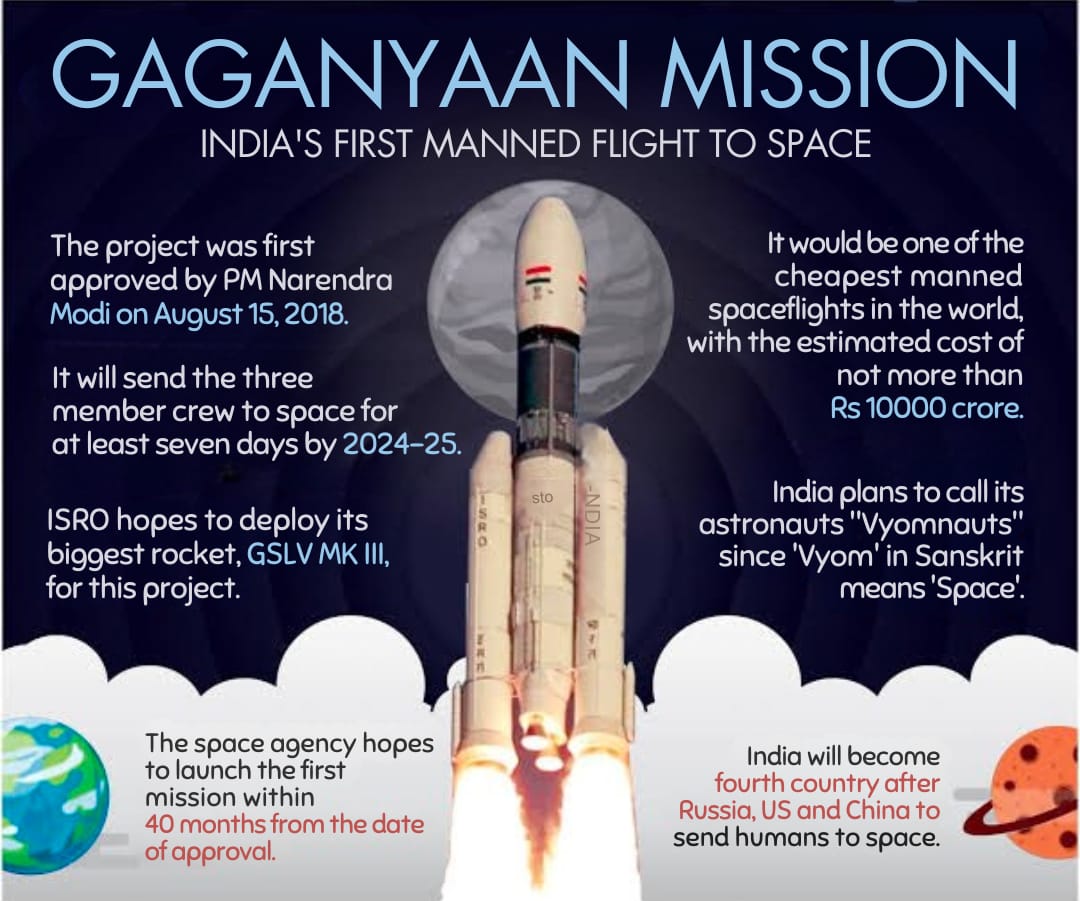
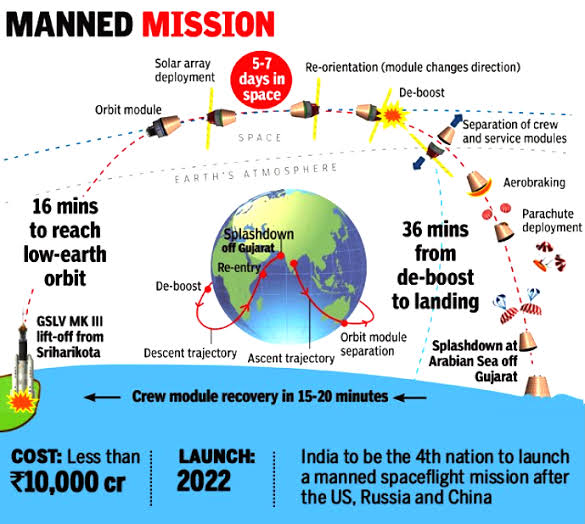
The Gaganyaan mission is India's ambitious project aimed at sending humans to space. Spearheaded by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), Gaganyaan aims to establish India as a significant player in human space exploration. This article provides an overview of the mission's objectives, technical aspects, challenges, and future prospects.
Objectives
The primary objectives of the Gaganyaan mission are:
- Human Spaceflight Capability: Develop the capability to send humans to low Earth orbit (LEO) and bring them back safely.
- Technological Advancements: Advance various technologies, including life support systems, crew safety, and emergency rescue mechanisms.
- International Collaboration: Collaborate with international space agencies and organizations to enhance technical know-how and resource sharing.
Technical Aspects
Launch Vehicle
- GSLV Mk III: The Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III (GSLV Mk III), also known as LVM-3, is the designated launch vehicle for the Gaganyaan mission. It is a three-stage heavy-lift rocket designed to carry substantial payloads into space.
- Modifications: The GSLV Mk III will be modified to ensure crew safety and accommodate the crew module.
Crew Module
- Design: The crew module, designed to carry three astronauts, is equipped with advanced life support systems, environmental control, and monitoring systems.
- Safety Features: It includes features such as crew escape systems, redundant safety measures, and robust thermal protection to ensure the astronauts' safety during all phases of the mission.
Environmental Control and Life Support System (ECLSS)
- Functionality: The ECLSS is critical for maintaining a habitable environment inside the crew module. It regulates temperature, humidity, and oxygen levels, and removes carbon dioxide and other contaminants.
- Development: ISRO is developing indigenous ECLSS technology, incorporating inputs from international collaborators.
Challenges
- Technological Hurdles: Developing reliable life support systems, ensuring crew safety, and achieving precise mission control are significant technological challenges.
- Budget Constraints: Balancing the mission's budget while achieving the desired technological advancements and safety standards requires careful planning and resource allocation.
- Risk Management: Ensuring the safety of astronauts in space and during re-entry involves meticulous risk assessment and management.
Future Prospects
- Manned Lunar Missions: Following the successful completion of the Gaganyaan mission, ISRO aims to undertake manned lunar missions, furthering India's presence in space exploration.
- Space Station Participation: India plans to participate in international space station programs and eventually develop its own space station.
- Space Science and Research: The mission will significantly boost space science and research in India, fostering advancements in various scientific fields.
Conclusion
The Gaganyaan mission represents a monumental step for India in the realm of human spaceflight. By developing indigenous technologies, ensuring rigorous safety measures, and fostering international collaborations, ISRO is paving the way for India's future in space exploration. The success of Gaganyaan will not only enhance India's technological capabilities but also inspire a new generation of scientists and engineers.